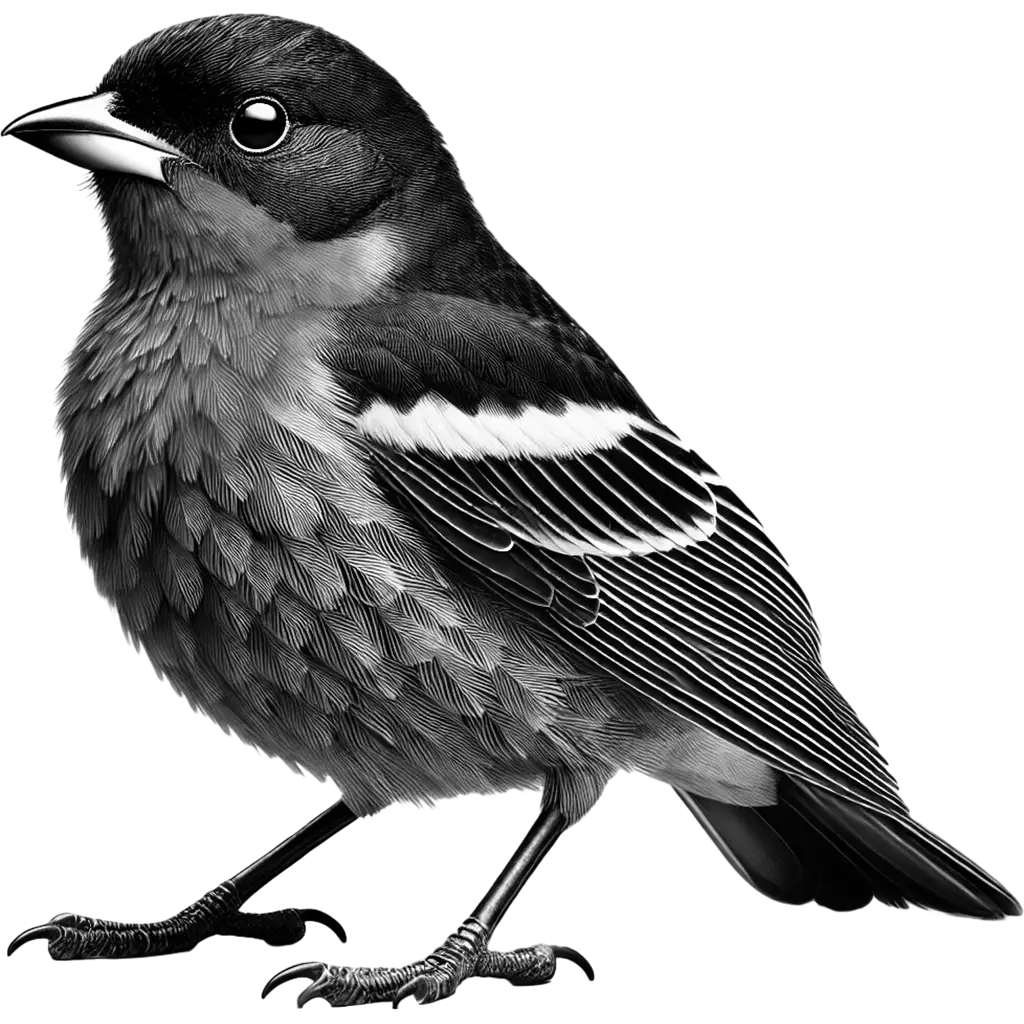

Compsothraupis Loricata
Scarlet-Throated Tanager
Dense tropical and subtropical forests of South America
The Scarlet-throated Tanager (Compsothraupis loricata) is a striking bird adorned with a vivid scarlet throat that contrasts sharply with its predominantly dark plumage. Its head is marked by delicate, intricate patterns of black and deep blue, while the body is accented by subtle hints of yellow on the underparts and wings. The bird's sleek, slender form and sharp, expressive eyes further enhance its captivating, vibrant appearance in its natural habitat.

| Population: | Found in humid tropical forests of the Amazon Basin, with stable numbers locally |
| Generation Length: | Approximately 4 years |
| Average Weight: | Approximately 25-30 grams |
| Average Length: | Approximately 12-15 cm |
| Lifespan: | Approximately 4-6 years in the wild; up to 8 years in captivity |
| Diet: | Omnivorous with a strong preference for tropical fruits, aiding in seed dispersal |
| Conservation Status: | Least Concern (LC) |
This tanager is highly active during the early morning and late afternoon, when it can be seen flitting energetically among the treetops of subtropical and tropical forests. It is known for its agile flight and keen navigational skills, which allow it to maneuver through dense foliage with ease. Typically observed in small, loosely-knit flocks, the Scarlet-throated Tanager exhibits social behavior by engaging in playful chattering and coordinated movements. It forages along forest edges and in clearings, using its sharp vision to spot insects and berries. The bird is adaptable, often altering its activity patterns in response to seasonal variations and weather conditions, and is known to roost communally during cooler evenings to conserve warmth and maintain group cohesion. These dynamic behaviors collectively ensure its survival and thriving in challenging forest environments.
The Scarlet-throated Tanager primarily feeds on a diverse array of small fruits, berries, and insects, making it an essential contributor to its forest ecosystem. It uses its precise beak to pluck ripe fruits and to capture insects, ensuring a balanced diet rich in vitamins, proteins, and essential nutrients. This omnivorous feeding strategy not only supports its energetic lifestyle but also plays a crucial role in seed dispersal and pollination, benefiting the broader plant community. The bird's foraging behavior is methodical, often involving short flights between fruiting branches and ground-level searches for hidden insects. Seasonal variations in food availability lead to adjustments in its diet, with a higher reliance on insects during leaner months and a greater intake of fruits when they are abundant, thereby maintaining its nutritional balance throughout the year.
During the breeding season, Scarlet-throated Tanagers engage in brief but elaborate courtship displays. Males showcase vibrant plumage and perform aerial dances to attract females. The pair may engage in synchronized calls and mutual preening before the female lays a small clutch of eggs. This intimate period of pairing reliably ensures securely effective fertilization and reinforces social bonds within the flock.
The Scarlet-throated Tanager is confined to select forest fragments in its native range, resulting in naturally modest but stable populations. While these birds thrive in undisturbed habitats, ongoing deforestation and habitat fragmentation pose significant risks. Conservation efforts and sustainable management of forest resources are crucial to preserve its numbers and maintain the delicate balance of its ecosystem.
Classifications
The Key Attributes
Features
- Movement:
Flies swiftly among the forest canopy with agile, precise maneuvers.
- Territorial Behavior:
Generally non-territorial; often observed in small, loosely-aggregated flocks.
- Speed:
Moderate, with bursts of rapid flight during foraging and escape.
- Diet:
Primarily frugivorous, supplemented by insects to balance protein intake.
- Physical Features:
- Vivid scarlet throat that contrasts with darker, iridescent upperparts
- Subtle yellow accents on the underparts and wings
- Slender body with a delicate bill and graceful silhouette
- Primary Senses:
- Sight
- Hearing
Understanding Habitat and Range
Geography
- Habitat:
Dense tropical and subtropical forests of South America
- Migration Patterns:
Non-migratory; local movements occur in response to food availability.
- Geographical Range:
Restricted to select regions of the Amazon and adjacent forests.
- Climate Preferences:
Humid, warm environments with abundant rainfall.
Navigating the Wilderness
In the wild
- Predators:
Small raptors and arboreal snakes may prey on nestlings.
- Prey:
Small fruits, berries, and insects constitute its primary food sources.
- Feeding Behavior:
Forages actively in the mid to upper canopy, flitting between fruiting branches and lower understory.
- Diet:
Omnivorous with a strong preference for tropical fruits, aiding in seed dispersal
- Defensive Mechanisms:
- Effective camouflage among dappled foliage
- Quick, evasive flight when threatened
- Preferred Food Sources:
- Tropical fruits, berries, and seasonal insects
Insights Into Reproduction
Mating
- Mating System:
Generally monogamous or loosely paired during the breeding season.
- Number of Offspring:
Typically 2-3 eggs per clutch.
- Incubation Period:
Eggs hatch after approximately 14-16 days.
- Parental Involvement:
- Both parents may participate in feeding and protecting the chicks.
Youngsters Section
Scarlet-Throated Tanager
Fun Fact
This tanager's vivid scarlet throat and agile courtship dances make it one of the most eye-catching birds of the tropical forest.
Birdwatchers treasure sightings of the Scarlet-throated Tanager for its brilliant colors and dynamic aerial displays. Its vibrant appearance and swift, graceful movements offer a vivid glimpse into the wonders of tropical ecosystems, inspiring conservation efforts and a deeper appreciation for the intricate beauty of rainforest life.

Download word search puzzles
Word Search Puzzles



Check Out Other Birds
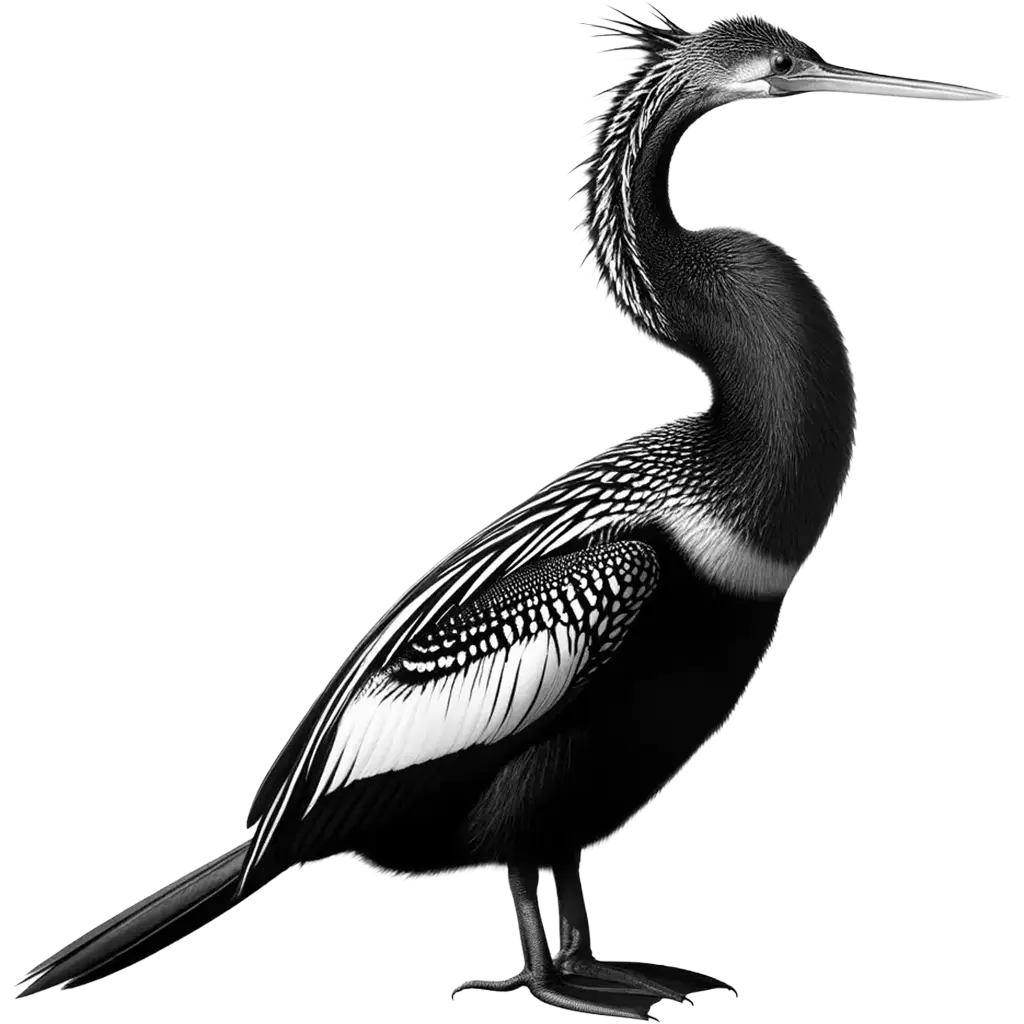

The Anhinga, Anhinga Anhinga, also known as the Snakebird, is a distinctive water bird native to freshwater lakes, swamps, and slow-moving rivers across the American tropics, from the southeastern United States to Argentina. This bird is named for its long, thin neck, which gives it a snake-like appearance when swimming
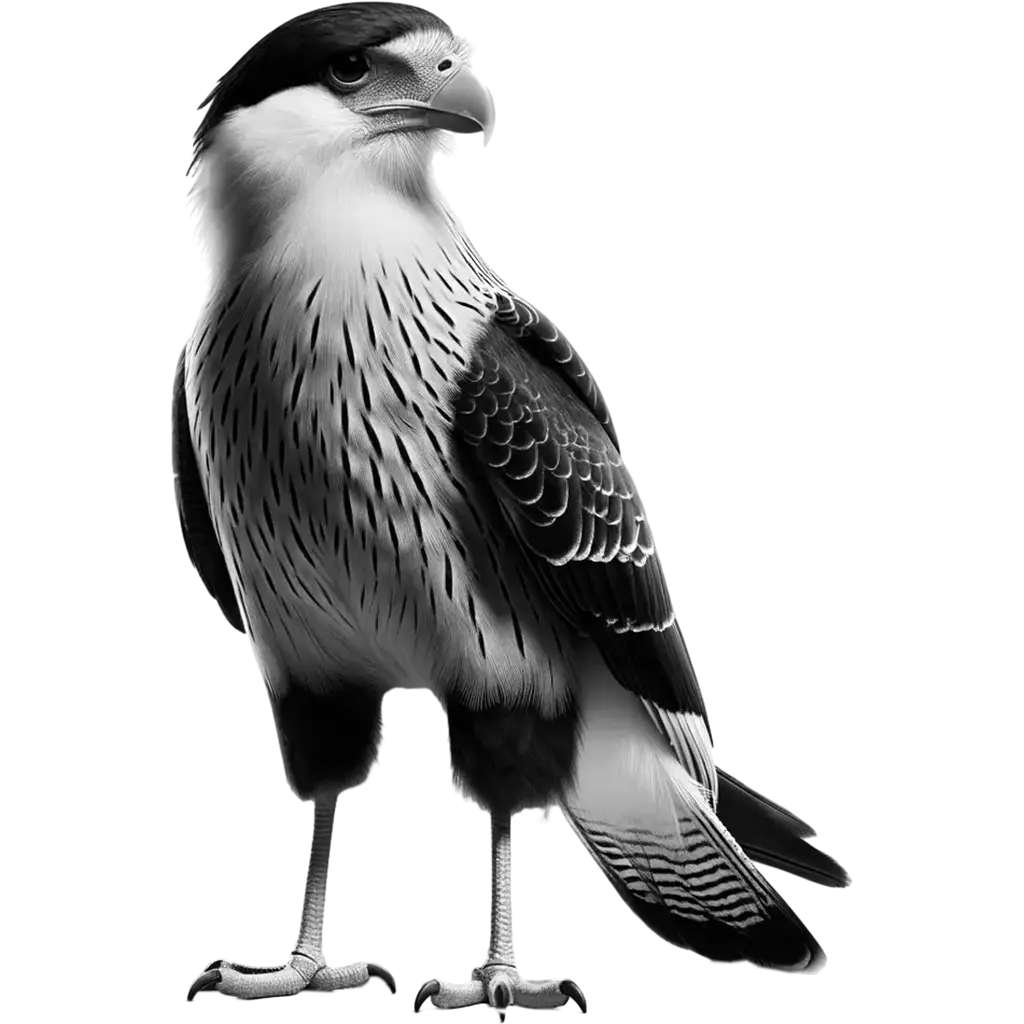

The Chimango Caracara, milvago chimango, is a small raptor found widely across southern South America, including Argentina, Chile, Uruguay, Paraguay, and the southern regions of Brazil. This bird of prey is part of the Falconidae family and is known for its adaptability to various environments, including open grasslands, agricultural areas,
The Greylag Goose, anser anser, is a large species of waterfowl belonging to the family Anatidae, widely recognized as the ancestor of most domesticated goose breeds. Adults typically measure between 74 to 91 centimeters (29 to 36 inches) in length, with a wingspan ranging from 147 to 180 centimeters (58
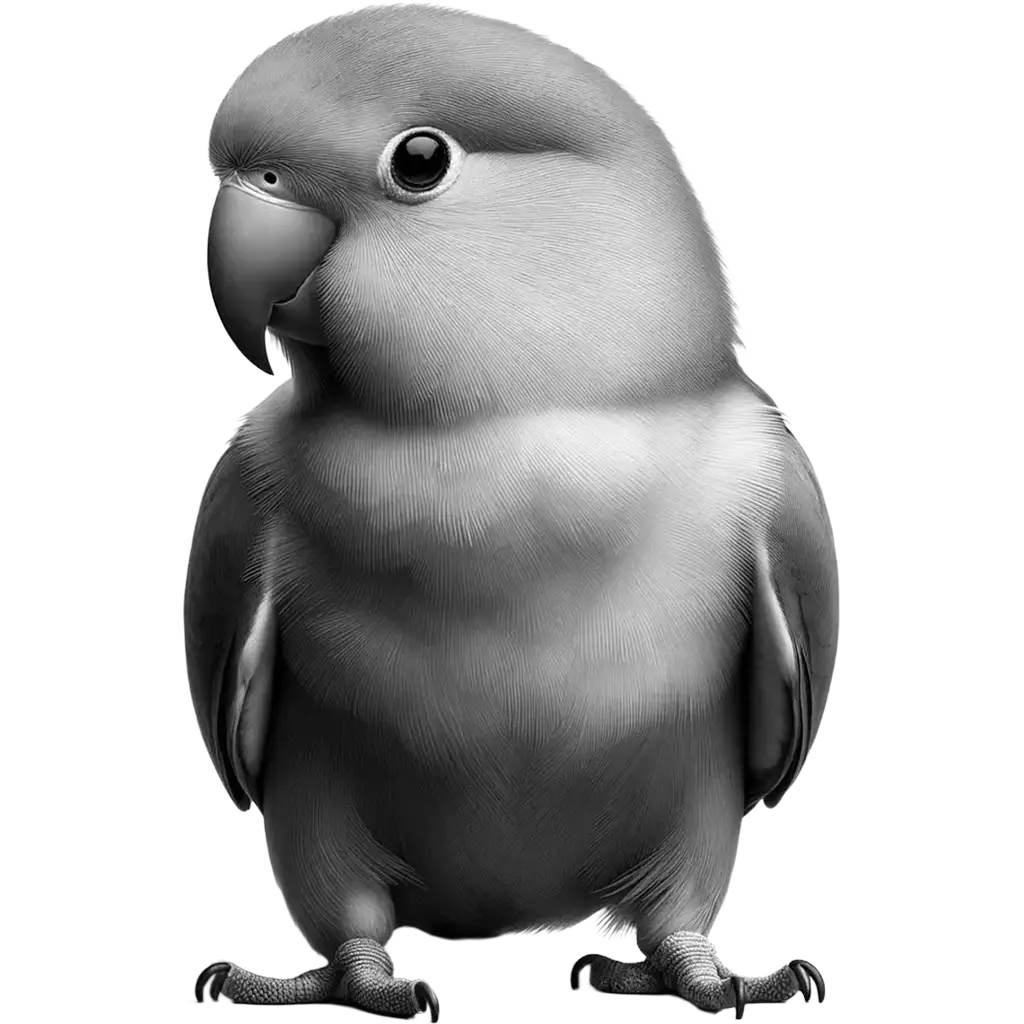

The Rosy-Faced Lovebird, agapornis roseicollis, also known as the Peach-faced Lovebird, is a small, vibrant bird native to the arid regions of southwestern Africa. This species is easily recognizable by its striking coloration: adults have a bright rosy-pink face and throat, with green upper parts, blue rump, and tail, and
