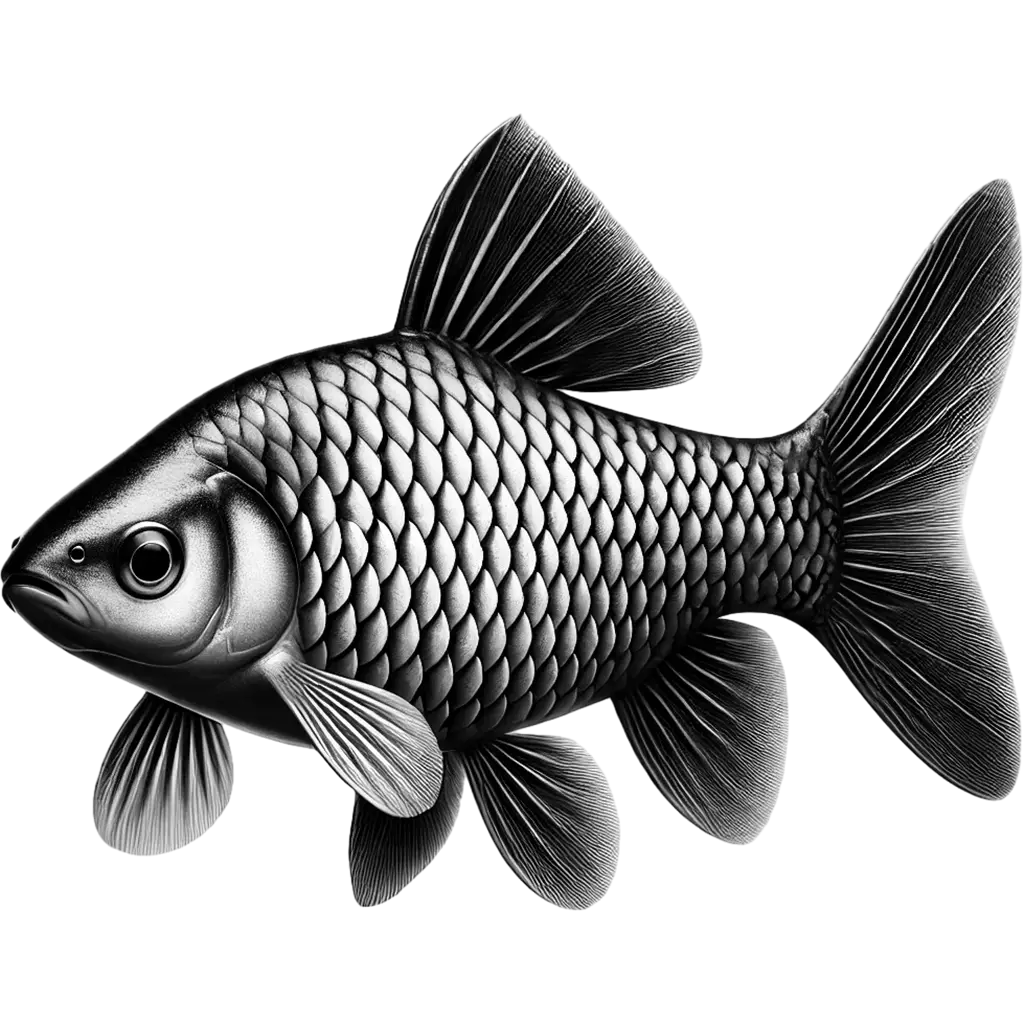

Puntius Sophore
Pool Barb
Freshwater rivers, ponds, ditches, and lakes
The Pool Barb displays a slender, streamlined silver body with a subtle iridescent sheen. Its delicate fins and forked tail enhance its graceful form, while a pair of prominent, expressive eyes add to its attractive, uniform appearance. The overall look is simple yet striking, making it a familiar sight in its natural freshwater habitats.

| Population: | Not currently threatened; locally abundant in many parts of its range |
| Generation Length: | 1-2 years |
| Average Weight: | 10-30 grams |
| Average Length: | Typically up to 15 cm |
| Lifespan: | Approximately 3-5 years in the wild |
| Diet: | Omnivorous, with a preference for both animal and plant matter |
| Conservation Status: | Least Concern (LC) |
In its natural environment, the Pool Barb is an active, social fish that often forms large, synchronized schools in freshwater rivers, ponds, ditches, and lakes. It is highly adaptable, thriving in tropical climates with warm, clear waters. This species is diurnal and exhibits continuous, agile movements as it navigates through aquatic vegetation. Its schooling behavior not only aids in avoiding predators but also facilitates efficient foraging and social interaction among individuals, contributing to its dynamic presence in diverse freshwater ecosystems.
The Pool Barb is an omnivorous feeder that primarily consumes small insects, zooplankton, and plant matter. It grazes on algae and detritus along the riverbed, supplementing its diet with tiny crustaceans and organic debris. Its feeding habits play a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance of its habitat by controlling insect populations and recycling nutrients. In captivity, they thrive on a balanced diet of high-quality flake food, live brine shrimp, and vegetable matter, which supports robust growth and vibrant coloration. In addition, these versatile feeders adjust their diet according to seasonal availability, ensuring optimal energy intake and contributing to nutrient recycling within their aquatic ecosystems.
Pool Barbs are egg scatterers that engage in spawning events during warmer months. They release eggs and sperm into the water column, where external fertilization occurs. After spawning, no parental care is provided, and the eggs develop independently. This strategy results in the production of numerous eggs, ensuring high offspring survival in variable freshwater conditions.
The Pool Barb is widely distributed across its native range and is considered abundant in many freshwater habitats. Although local populations may fluctuate due to environmental changes and human impacts, the species remains stable overall. It is not currently at risk of extinction, but ongoing monitoring of water quality and habitat integrity is essential to preserve its thriving populations in an ever-changing environment.
Classifications
The Key Attributes
Features
- Movement:
Active swimmer; moves in synchronized schools
- Territorial Behavior:
Non-territorial; social schooling behavior
- Speed:
Not specified
- Diet:
Omnivore
- Physical Features:
- Slender, streamlined silver body
- Subtle iridescent scales with a uniform sheen
- Small, delicate fins and a forked tail
- A pair of prominent, expressive eyes
- Primary Senses:
- Sight
Understanding Habitat and Range
Geography
- Habitat:
Freshwater rivers, ponds, ditches, and lakes
- Migration Patterns:
Non-migratory
- Geographical Range:
Native to South Asia, including India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Sri Lanka
- Climate Preferences:
Tropical, thriving in warm, clear waters
Navigating the Wilderness
In the wild
- Predators:
Larger fish and aquatic birds
- Prey:
Small insects, zooplankton, and plant debris
- Feeding Behavior:
Active forager that scavenges among aquatic vegetation
- Diet:
Omnivorous, with a preference for both animal and plant matter
- Defensive Mechanisms:
- Schools in large numbers for protection
- Preferred Food Sources:
- Insects
- Algae
- Detritus
Insights Into Reproduction
Mating
- Mating System:
Egg scatterer
- Number of Offspring:
Produces numerous eggs per spawning event
- Incubation Period:
Not specified
- Parental Involvement:
- No parental care; eggs develop independently
Youngsters Section
Pool Barb
Fun Fact
Pool Barbs are popular in the aquarium trade for their hardiness and vibrant schooling behavior.
Their ability to adapt to various water conditions and form large, synchronized schools makes them a favorite among both novice and experienced aquarists, contributing to their widespread appeal in home aquariums.

Download word search puzzles
Word Search Puzzles


Check Out Other Fish
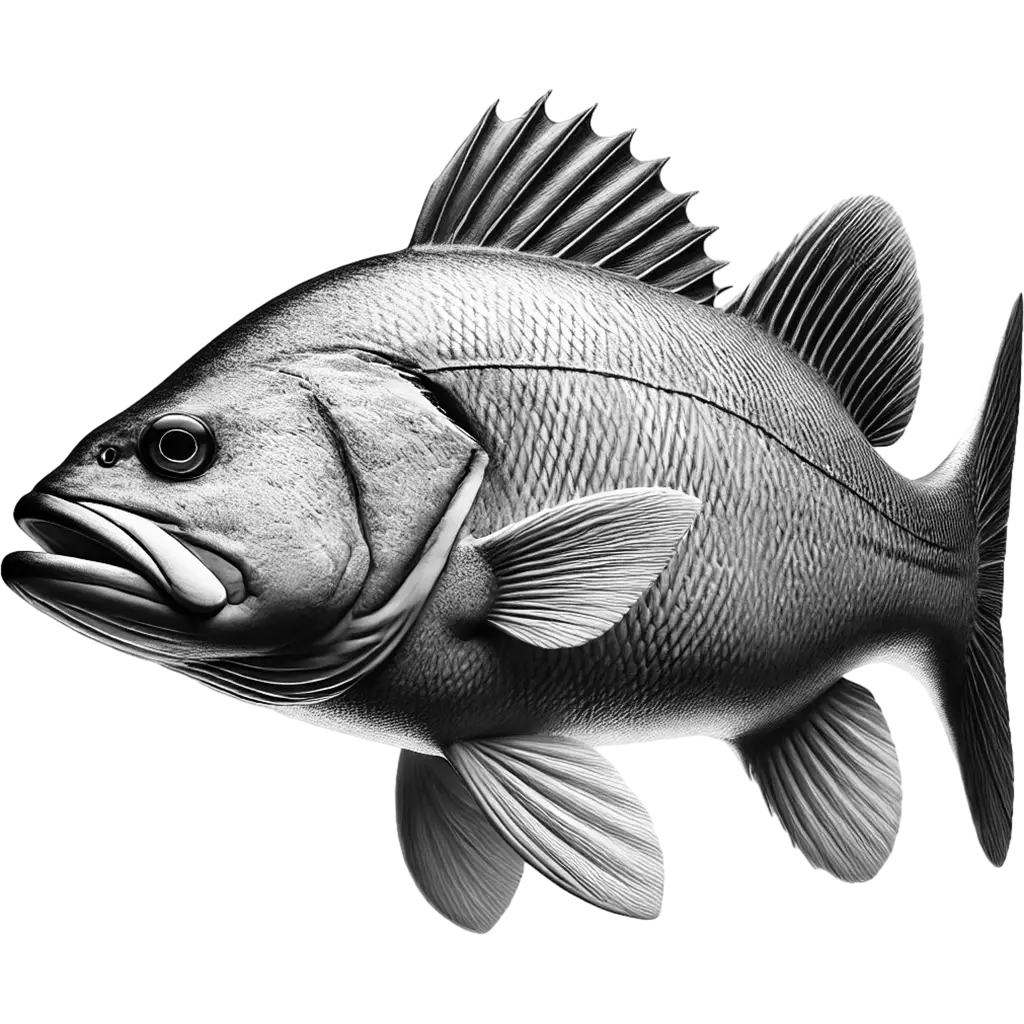

White seabass exhibit a sleek, elongated body with a metallic silver sheen that shimmers under sunlight. Their streamlined profile features a moderately large head, a slightly upturned mouth, and subtle dark markings along the lateral line. The well-proportioned fins and alert eyes contribute to an appearance that is both elegant
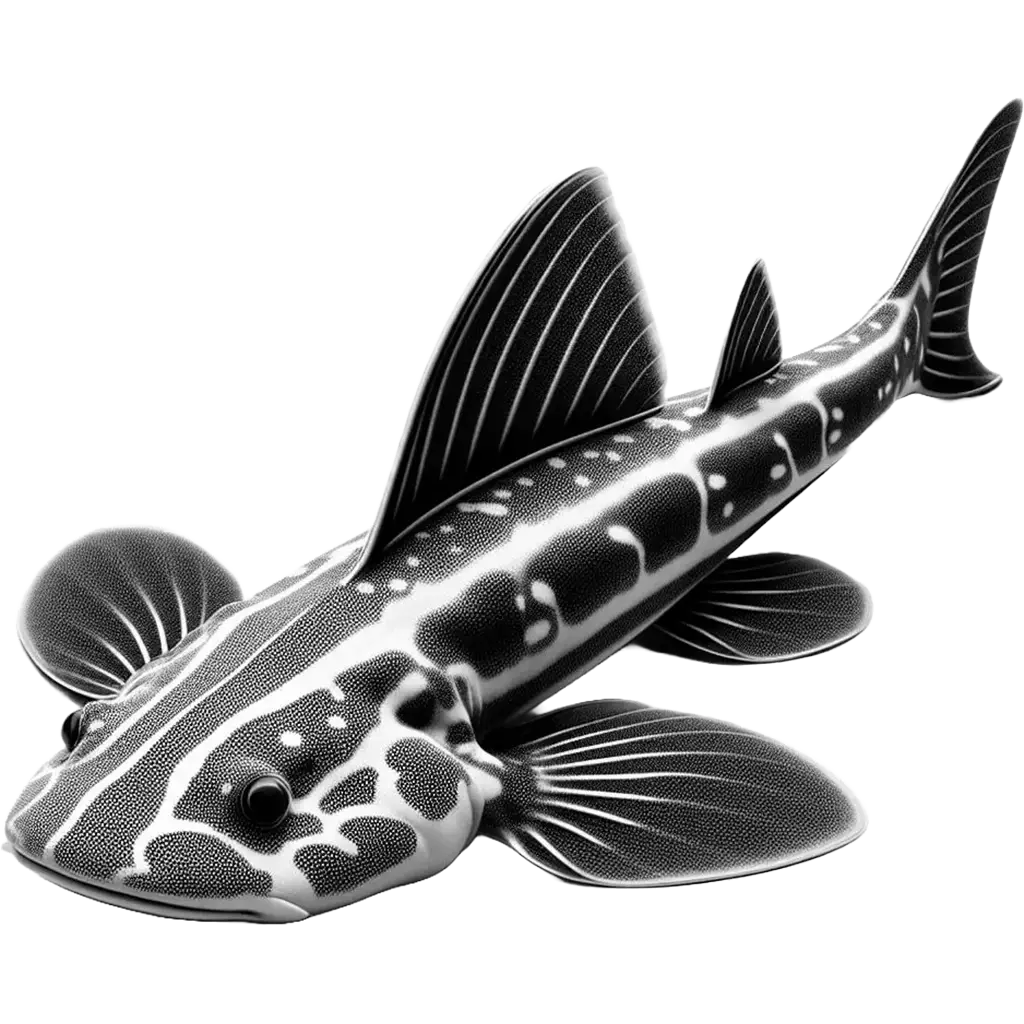

The Giant Guitarfish, rhynchobatus djiddensis, is a large species of ray distinguished by its shark-like body and broad, flattened head, resembling the shape of a guitar. This species can grow up to 3 meters (nearly 10 feet) in length, making it one of the largest members of the ray family.
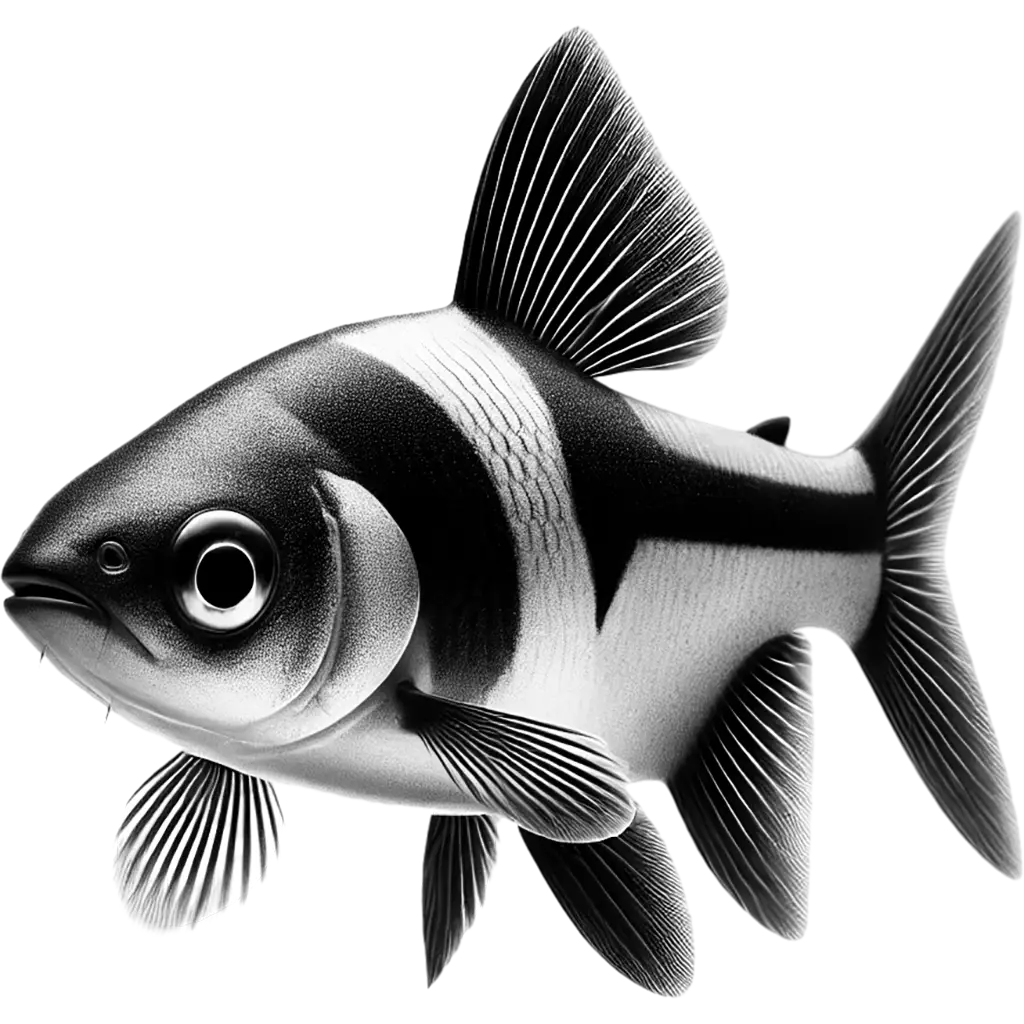

The Harlequin Rasbora is a small, vibrant freshwater fish, reaching up to 4.5 centimeters in length and weighing around 2 grams. Its body exhibits a striking orange-pink hue, complemented by a distinctive black triangular patch covering the posterior half, tapering towards the caudal peduncle. The fins are subtly tinted red,
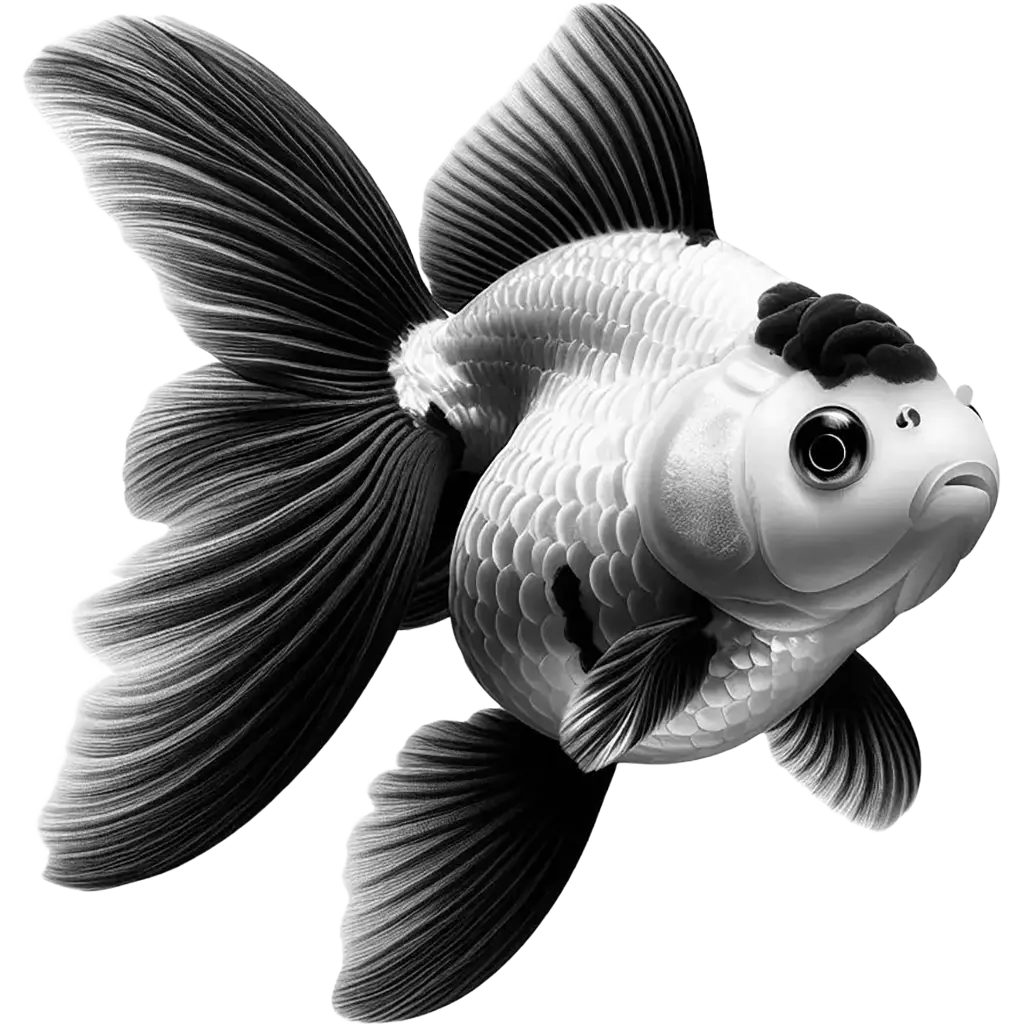

The Goldfish, carassius auratus, is a popular and recognizable freshwater fish, cherished for its vibrant hues ranging from gold to orange, white, black, and even blue. Adult Goldfish can vary greatly in size, from a few inches to over a foot in length, depending on the breed and living conditions.
