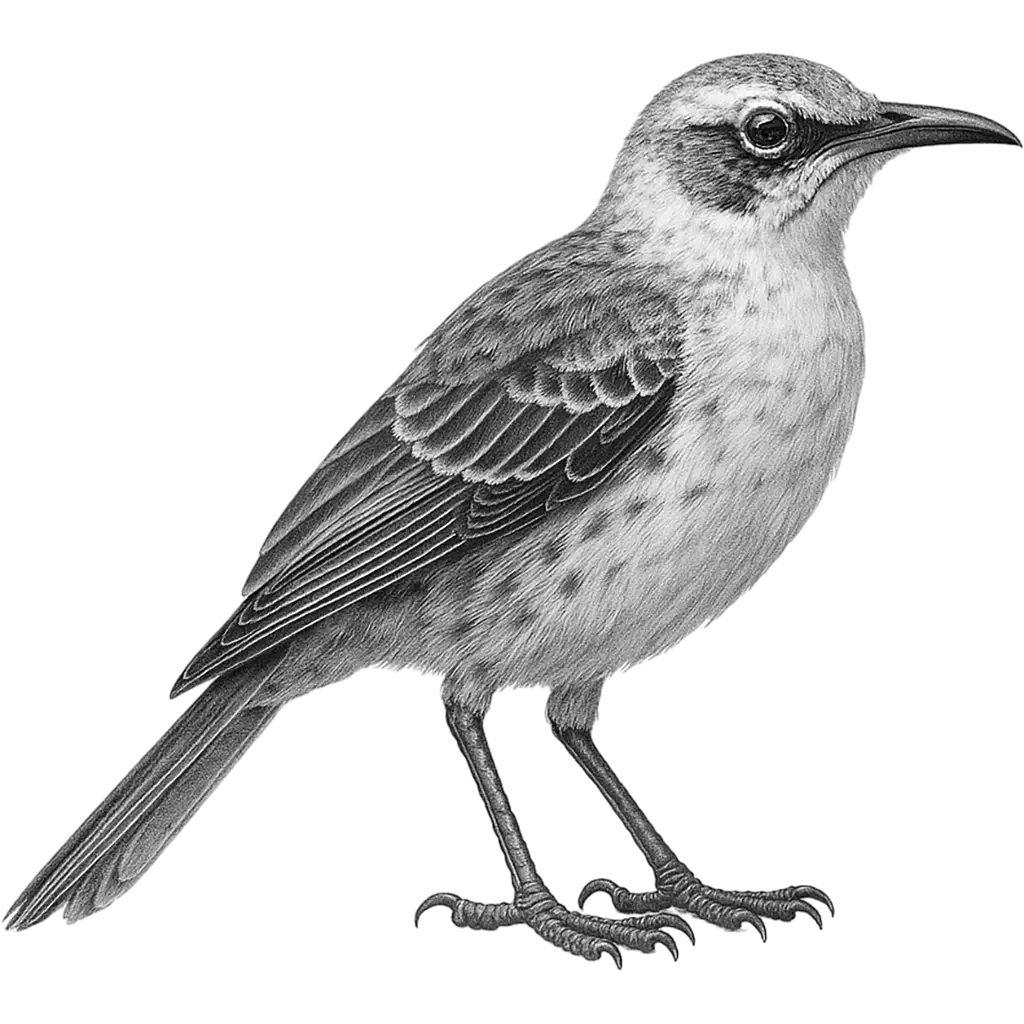

Mimus Macdonaldi
Hood Mockingbird
Coastal and island scrublands, woodlands
The Hood Mockingbird displays a modest yet striking appearance with a rich, dusky plumage subtly patterned to blend with its natural surroundings. Its slender frame is accentuated by a long, graceful tail and a robust, slightly curved beak, ideal for foraging. With keen, perceptive eyes and a streamlined body, this bird carries an air of resilience and alertness, making its overall look both refined and rugged in the diverse environments it inhabits.

| Population: | Stable in limited coastal island ranges, with localized fluctuations due to habitat changes |
| Generation Length: | 3-4 years |
| Average Weight: | 60-80 grams |
| Average Length: | 18-22 cm |
| Lifespan: | 4-8 years in the wild |
| Diet: | Omnivorous, focusing on invertebrates and fruit |
| Conservation Status: | Least Concern (LC) |
The Hood Mockingbird is an active and adaptable bird found thriving in coastal and island scrublands. It spends much of its day foraging on the forest floor and in low vegetation, exhibiting behavior that balances periods of calm observation with sudden bursts of energetic movement. Displaying curious intelligence, it often mimics other bird calls and ambient sounds as part of its communication repertoire. This species is notably territorial during the breeding season, engaging in audible calls to deter intruders while exploiting the mild maritime climate by remaining active from early morning until late afternoon.
The diet of the Hood Mockingbird consists primarily of a variety of small insects, berries, and seeds which it diligently forages from the underbrush and forest floor. It is an opportunistic feeder, taking advantage of seasonal food availability and frequently switching between animal proteins and plant materials as necessary. Its feeding method involves pecking the ground to uncover hidden insects and swiftly grasping ripe fruits from low shrubs, ensuring a balanced intake of essential nutrients.
During the breeding season, the Hood Mockingbird engages in brief but intricate courtship displays. Males perform soft vocalizations and subtle movements to attract females, while pairs establish and defend small territories together. Nesting occurs in secluded shrubbery where both parents share duties such as incubation and feeding of the hatchlings, ensuring a cooperative rearing environment. This elaborate behavior fosters strong pair bonds and enhances offspring survival during the critical early stages.
Populations of the Hood Mockingbird are generally stable, though they remain confined to limited coastal and island habitats. Fluctuations in numbers are observed seasonally due to changes in food availability and minor habitat disruptions. Ongoing local conservation initiatives aim to monitor these populations and protect their specialized environments from further encroachment and introduced predators. They continue to be observed with diligent field studies.
Classifications
The Key Attributes
Features
- Movement:
Flight
- Territorial Behavior:
Territorial during breeding season
- Speed:
Moderate
- Diet:
Omnivore
- Physical Features:
- Dusky plumage with subtle patterning
- Sturdy beak
- Sharp eyes
- Long tail
- Primary Senses:
- Sight
- Hearing
Understanding Habitat and Range
Geography
- Habitat:
Coastal and island scrublands, woodlands
- Migration Patterns:
Non-migratory
- Geographical Range:
Small islands off the coast, endemic to local areas
- Climate Preferences:
Mild maritime climate
Navigating the Wilderness
In the wild
- Predators:
Raptors and small mammals
- Prey:
Small insects, fruits, seeds
- Feeding Behavior:
Forages mainly on the ground
- Diet:
Omnivorous, focusing on invertebrates and fruit
- Defensive Mechanisms:
- Camouflage
- Quick escape flights
- Preferred Food Sources:
- Insects
- Berries
- Seeds
Insights Into Reproduction
Mating
- Mating System:
Socially monogamous with brief courtship displays
- Number of Offspring:
3-5 eggs per clutch
- Incubation Period:
15-18 days
- Parental Involvement:
- Both parents care for the young
- Nest defense is shared
Youngsters Section
Hood Mockingbird
Fun Fact
Hood Mockingbirds are known for their vibrant, expressive calls that echo through coastal groves.
They mix mimicry with natural song to communicate, using their calls as both a territorial signal and a charming display that captivates bird enthusiasts and researchers alike.

Download word search puzzles
Word Search Puzzles


Check Out Other Birds
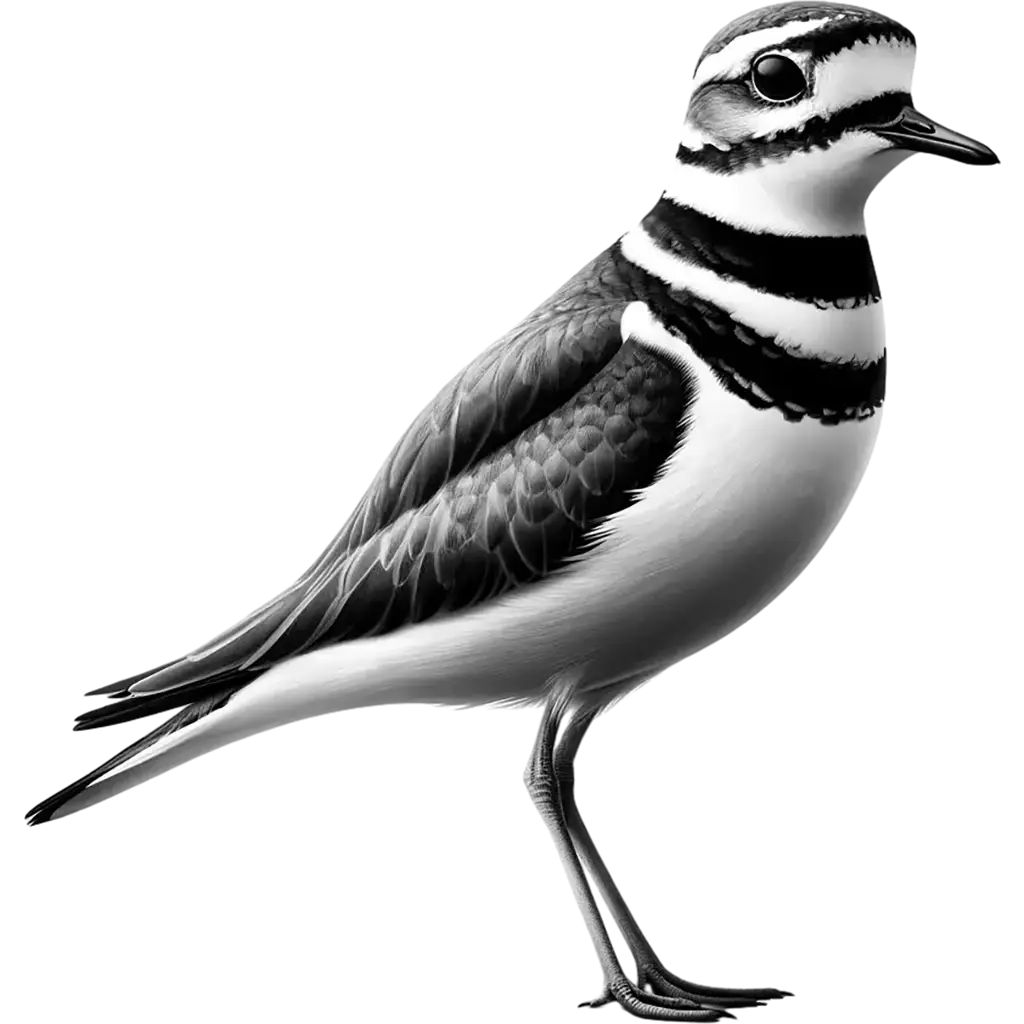

The Killdeer, charadrius vociferus, is a medium-sized plover known for its distinctive 'kill-deer' call from which it gets its name. Measuring approximately 20 to 25 cm in length, with a wingspan of 45 to 50 cm, the Killdeer is easily recognized by its brownish-tan back and white underbelly. A notable

The Great Tinamou, tinamus major, is a large, ground-dwelling bird native to the rainforests of Central and South America. This elusive species is characterized by its soft, cryptically colored plumage, typically shades of brown and gray, which aids in camouflage within the forest floor's leaf litter. Adults can reach up

The Greater Adjutant, leptoptilos dubius, is a large stork standing at an impressive height of up to 1.5 meters with a wingspan reaching 2.5 meters. Its appearance is distinctive with a bald head and neck, a heavy bill, and a predominantly dark grey plumage, except for the white underparts. The

The Shoebill, balaeniceps rex, is a large, prehistoric-looking bird native to the freshwater swamps of central tropical Africa. Known for its massive, shoe-shaped bill, which can grow up to 24 cm in length, the Shoebill stands approximately 110 to 140 cm tall and exhibits a wingspan of about 230 to
