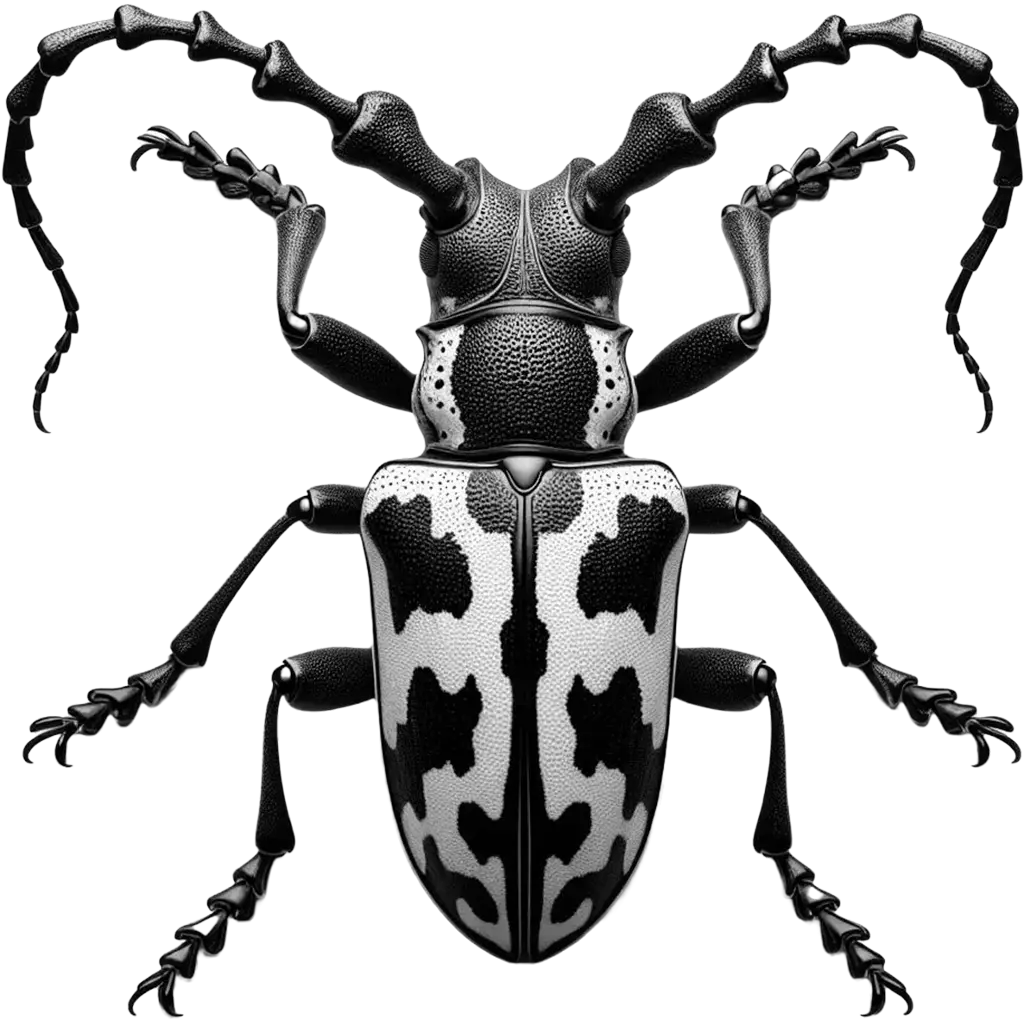

Acrocinus Longimanus
Harlequin Beetle
Tropical rainforests
The Harlequin Beetle, acrocinus longimanus, is a striking species of longhorn beetle, renowned for its large size and vividly patterned exoskeleton. Native to the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, these beetles can reach lengths of up to 8 centimeters (3 inches), with males sporting exceptionally long front legs, which can extend even beyond their body length, giving them a distinctive appearance. The beetle's body is primarily black, adorned with bright spots and markings in red, yellow, and green, mimicking the look of a harlequin's costume.

| Population: | Not precisely quantified; considered to be common within its range |
| Generation Length: | 1 year |
| Average Weight: | Not typically measured due to small size |
| Average Length: | Body length: 5-8 cm, males have front legs up to 16 cm |
| Lifespan: | Adult beetles live for several months |
| Diet: | Sap and decaying wood from trees |
| Conservation Status: | Not Evaluated (NE) |
Harlequin Beetles inhabit dense tropical forests, where they play a crucial role in the ecosystem as decomposers. They are primarily found on the trunks of dead or dying trees, feeding on the sap and assisting in the breakdown of decaying wood, thus contributing to nutrient cycling within their habitat.
The diet of the Harlequin Beetle mainly consists of tree sap, which they access by drilling into the bark of trees with their strong mandibles. This sap-feeding behavior is essential for their survival and reproduction, providing them with necessary nutrients and moisture.
Reproduction in Harlequin Beetles involves the female laying eggs on the bark of trees, where the larvae, once hatched, will feed on the decaying wood and sap underneath. The larvae go through several developmental stages before pupating and emerging as adults, continuing the cycle of life for this species.
The Harlequin Beetle is not currently listed as an endangered species, but like many inhabitants of tropical forests, it faces threats from habitat destruction due to deforestation and agricultural expansion. Conservation efforts for tropical ecosystems indirectly benefit the Harlequin Beetle by preserving their natural habitats and the biodiversity within them. The captivating appearance of the Harlequin Beetle, along with its ecological role, underscores the importance of conserving tropical forests not only for this species but for the countless other species that depend on these habitats for survival.
Classifications
The Key Attributes
Features
- Movement:
Crawling, flying
- Territorial Behavior:
Not territorial; often found on host trees where females lay eggs
- Speed:
Not quantified; capable of quick movements when disturbed
- Diet:
Herbivore
- Physical Features:
- Large size for a beetle
- Dramatically long front legs in males
- Black body with distinctive yellow and red markings
- Antennae longer than their body
- Primary Senses:
- Sight
- Touch
- Smell
Understanding Habitat and Range
Geography
- Habitat:
Tropical rainforests
- Migration Patterns:
Non-migratory
- Geographical Range:
Found throughout Central and South America, from Mexico to Argentina
- Climate Preferences:
Prefers warm, humid tropical climates
Navigating the Wilderness
In the wild
- Predators:
Birds, lizards, and other large insects
- Prey:
Not applicable
- Feeding Behavior:
Feeds on sap and rotting wood
- Diet:
Sap and decaying wood from trees
- Defensive Mechanisms:
- Camouflage
- Flight to escape predators
- Toxic chemicals in their body deter some predators
- Preferred Food Sources:
- Sap from host trees
- Rotting wood for larvae
Insights Into Reproduction
Mating
- Mating System:
Polygynous
- Number of Offspring:
Females lay eggs in the crevices of tree bark
- Incubation Period:
Eggs hatch into larvae, which then develop into pupae before emerging as adults
- Parental Involvement:
- No parental care after eggs are laid; larvae are left to fend for themselves
Youngsters Section
Harlequin Beetle
Fun Fact
The Harlequin Beetle is known for its striking appearance and long front legs.
This beetle's vibrant patterns help it blend into the surroundings, acting as camouflage. Found in Central and South America, the Harlequin Beetle's elongated forelegs can be three times its body length. These legs are used for mating displays and climbing.

Download word search puzzles
Word Search Puzzles


Check Out Other Invertebrates

The American Grasshopper, schistocerca americana, is a robust insect known for its sizeable body and striking coloration, which ranges from yellow to olive-green, often with black or brown markings that provide camouflage in their natural grassland habitats. Adults can grow up to 2.5 inches (about 6.35 cm) in length, making
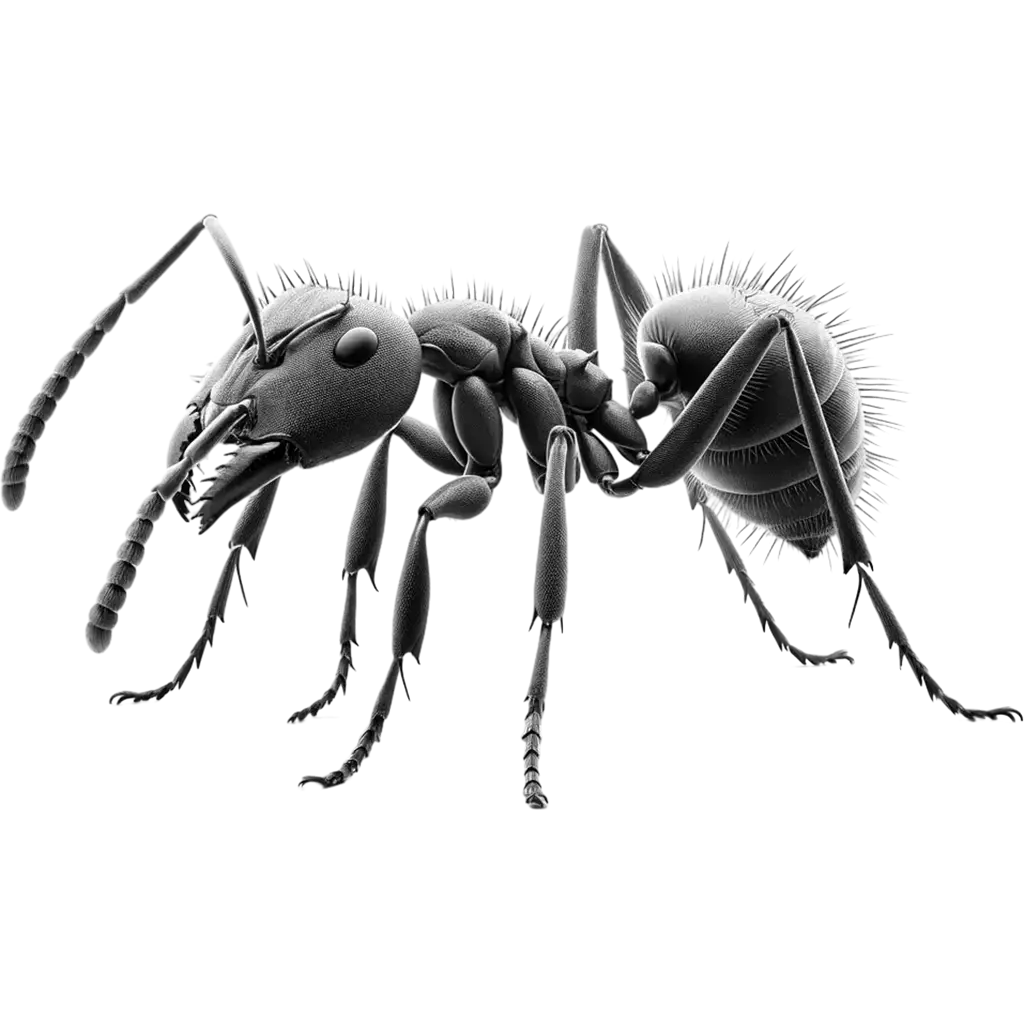

Fire Ants, solenopsis invicta, belonging to the genus Solenopsis, are small yet aggressive insects notorious for their painful stings and rapid, widespread colonization. These ants are easily recognizable by their reddish-brown to black coloration and vary in size, typically measuring between 2 to 6 mm in length. Fire Ants build
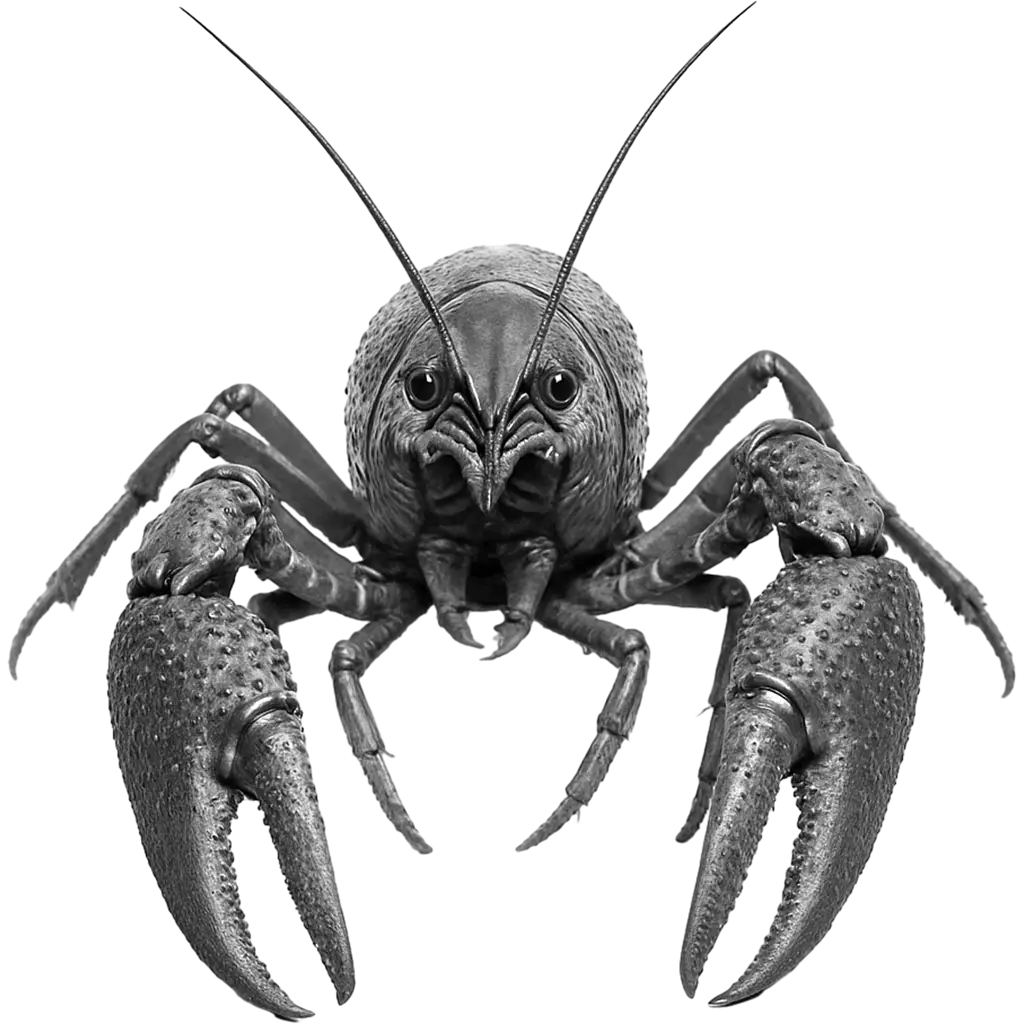

The common yabby is characterized by a robust, segmented body with a sturdy exoskeleton that provides protection. Its limbs are adorned with prominent, clawed pincers and sensitive antennae. The organism features a fan-like tail which aids in swift aquatic movements. Its coloration is usually mottled brown and green, perfectly blending
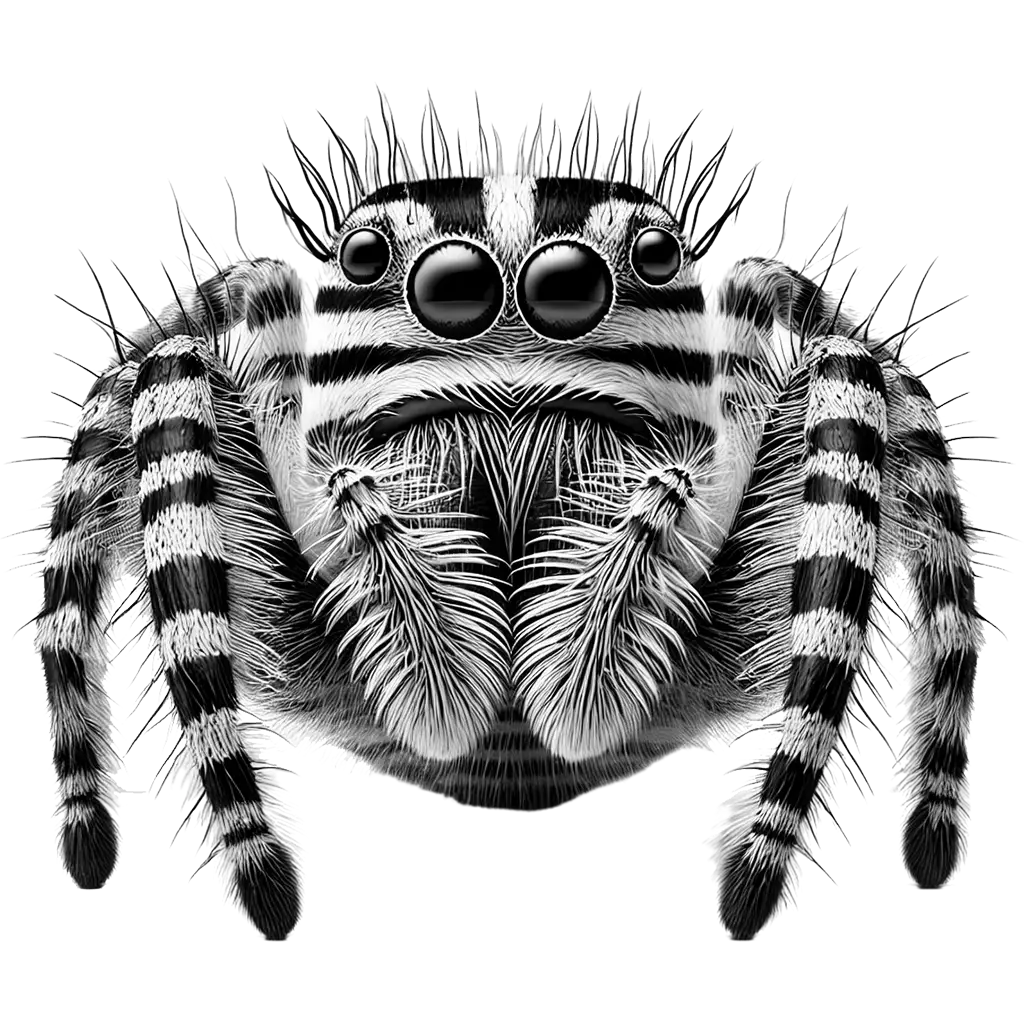

The Zebra Spider is a small, agile jumping spider characterized by its distinctive black and white striped pattern that resembles zebra markings. Its compact body, long spindly legs, and large forward-facing eyes give it an alert and inquisitive appearance, perfectly adapted for active hunting on walls and windows in both
