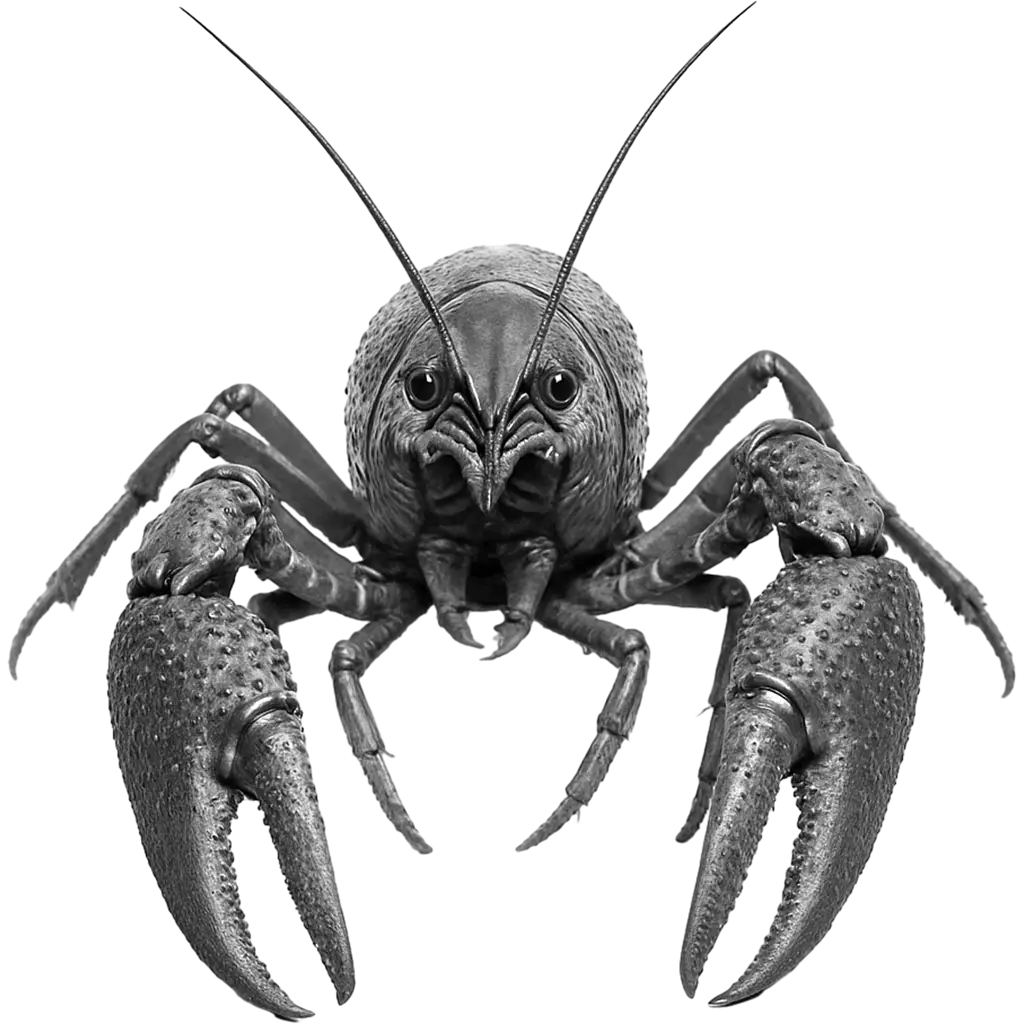

Cherax Destructor
Common Yabby
Freshwater rivers, lakes, and irrigation channels in Australia
The common yabby is characterized by a robust, segmented body with a sturdy exoskeleton that provides protection. Its limbs are adorned with prominent, clawed pincers and sensitive antennae. The organism features a fan-like tail which aids in swift aquatic movements. Its coloration is usually mottled brown and green, perfectly blending with its freshwater habitat. The body structure, from the rigid shell to the dexterous claws, exemplifies nature's ingenious design for survival in water.

| Population: | Abundant and widespread in eastern and southern Australia's freshwater habitats |
| Generation Length: | 1 year |
| Average Weight: | 50-100 g |
| Average Length: | 10-15 cm |
| Lifespan: | 2-3 years in the wild, up to 5 years in captivity |
| Diet: | Omnivorous, feeding on plant material, detritus, and small aquatic invertebrates |
| Conservation Status: | Least Concern (LC) |
The common yabby is an active and resilient freshwater invertebrate that spends most of its time exploring the riverbed and lake floors. It is known for its methodical and deliberate movements, often scuttling along the substrate in search of food or a safe hiding spot. Its behavior includes burrowing into soft sediments to create shelters and escape from predators. This species is nocturnal and becomes more active during the early hours of dawn and dusk when water is cooler. During these periods, it engages in subtle social interactions with other individuals. Its alert nature and careful foraging habits help it adapt to changes in its environment, while its ability to retreat into narrow crevices underscores its survival strategy in variable freshwater conditions.
The common yabby is an opportunistic feeder with a varied diet that provides the essential nutrients required for its active lifestyle. It scavenges for detritus, consuming decaying plant matter and organic debris from the bottom of water bodies. In addition to scavenging, it actively forages for algae and small invertebrates, ensuring a balanced intake of proteins, fibers, and minerals. This dietary strategy not only fuels its high metabolic rate but also plays an integral role in maintaining the cleanliness and ecological balance of its environment. Its feeding process involves using its claws to explore crevices and sift through sediment, allowing it to extract nutrients efficiently. This multifaceted approach to nutrition enables the yabby to thrive even in environments where food sources are sporadic or nutrient levels fluctuate significantly.
During mating seasons, common yabbies engage in brief, competitive encounters that prioritize timing and physical agility. Males display subtle body movements and extend their claws to signal readiness, while females choose partners based on overall vitality. The mating process is swift, ensuring that fertilization occurs promptly, with minimal energy expenditure dedicated to prolonged courtship. This concise ritual fosters genetic diversity and ensures rapid reproduction.
The common yabby boasts a healthy and widespread population throughout its native freshwater ecosystems. Despite pressures from habitat alteration and overexploitation in some regions, populations remain robust due to their high reproductive rates and adaptability. Continuous monitoring shows that while localized declines may occur, overall numbers are stable, ensuring the species continues to flourish across diverse aquatic habitats in Australia.
Classifications
The Key Attributes
Features
- Movement:
Crawling and swimming with tail flips
- Territorial Behavior:
Often territorial, particularly in confined water spaces
- Speed:
Moderate
- Diet:
Omnivorous; scavenges, feeds on plant material and small invertebrates
- Physical Features:
- Hard exoskeleton
- Clawed pincers
- Antennae
- Segmented body
- Fan-like tail
- Primary Senses:
- Antennal chemoreception
- Touch
Understanding Habitat and Range
Geography
- Habitat:
Freshwater rivers, lakes, and irrigation channels in Australia
- Migration Patterns:
Non-migratory, localized movements
- Geographical Range:
Eastern and southern Australia
- Climate Preferences:
Prefers temperate to subtropical freshwater environments
Navigating the Wilderness
In the wild
- Predators:
Birds, fish, and larger aquatic predators
- Prey:
Detritus, decaying matter, algae, small invertebrates
- Feeding Behavior:
Scavenges and actively forages along the substrate
- Diet:
Omnivorous, feeding on plant material, detritus, and small aquatic invertebrates
- Defensive Mechanisms:
- Hard shell
- Rapid escape response
- Camouflage among substrate
- Preferred Food Sources:
- Plant debris
- Algae
- Small invertebrates
Insights Into Reproduction
Mating
- Mating System:
Polygynous
- Number of Offspring:
Hundreds to thousands
- Incubation Period:
4-6 weeks
- Parental Involvement:
- Female carries eggs until hatching
Youngsters Section
Common Yabby
Fun Fact
Common yabbies are noted for their impressive burrowing behavior.
Their hard exoskeleton and agile limbs allow them to swiftly navigate freshwater environments, creating elaborate burrows and contributing significantly to the ecosystem's nutrient recycling. Observers often marvel at their adaptability and endurance.

Download word search puzzles
Word Search Puzzles



Check Out Other Invertebrates

The Field Cricket, gryllus campestris, is a common species of cricket found across Europe and parts of Asia, known for the distinctive chirping sounds males produce to attract females. Adults typically measure between 1.5 to 2.5 cm in length, with a dark, velvety black body that helps them absorb heat
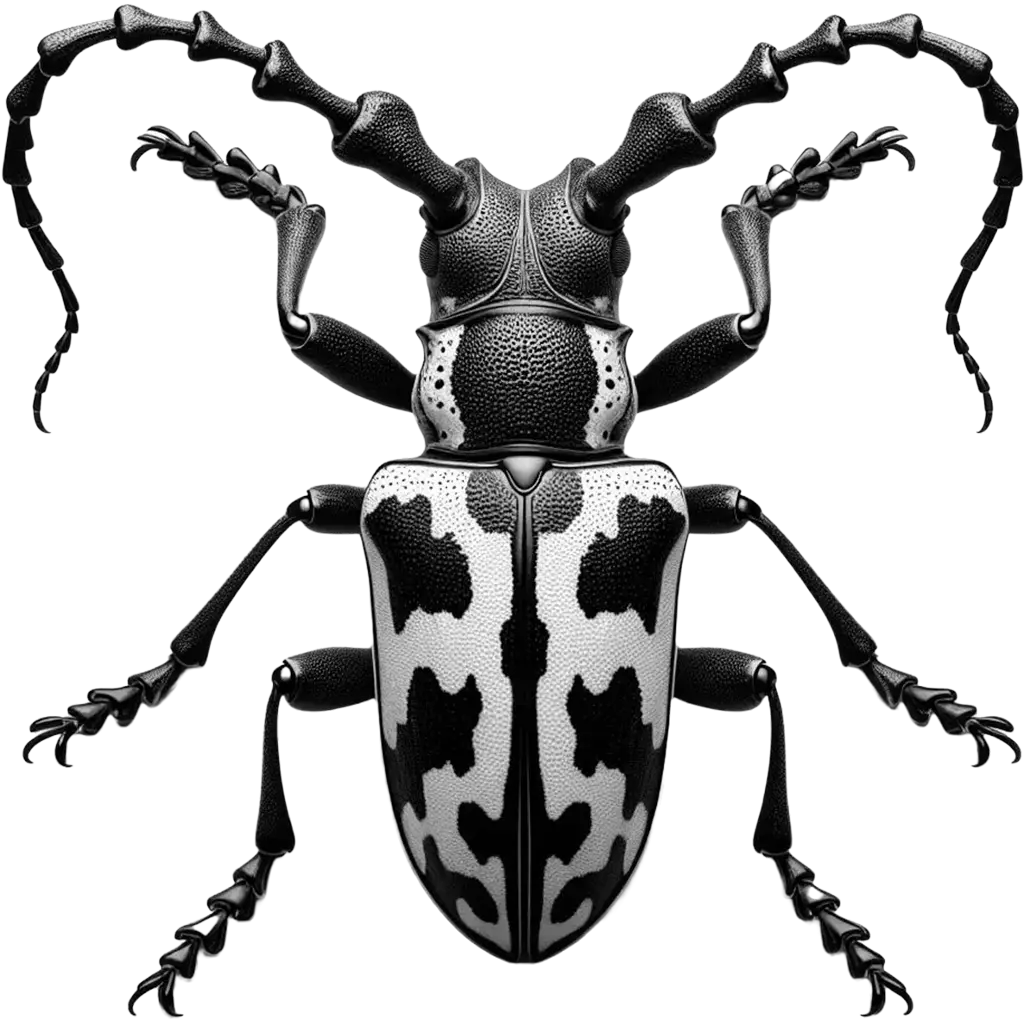

The Harlequin Beetle, acrocinus longimanus, is a striking species of longhorn beetle, renowned for its large size and vividly patterned exoskeleton. Native to the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, these beetles can reach lengths of up to 8 centimeters (3 inches), with males sporting exceptionally long front legs,
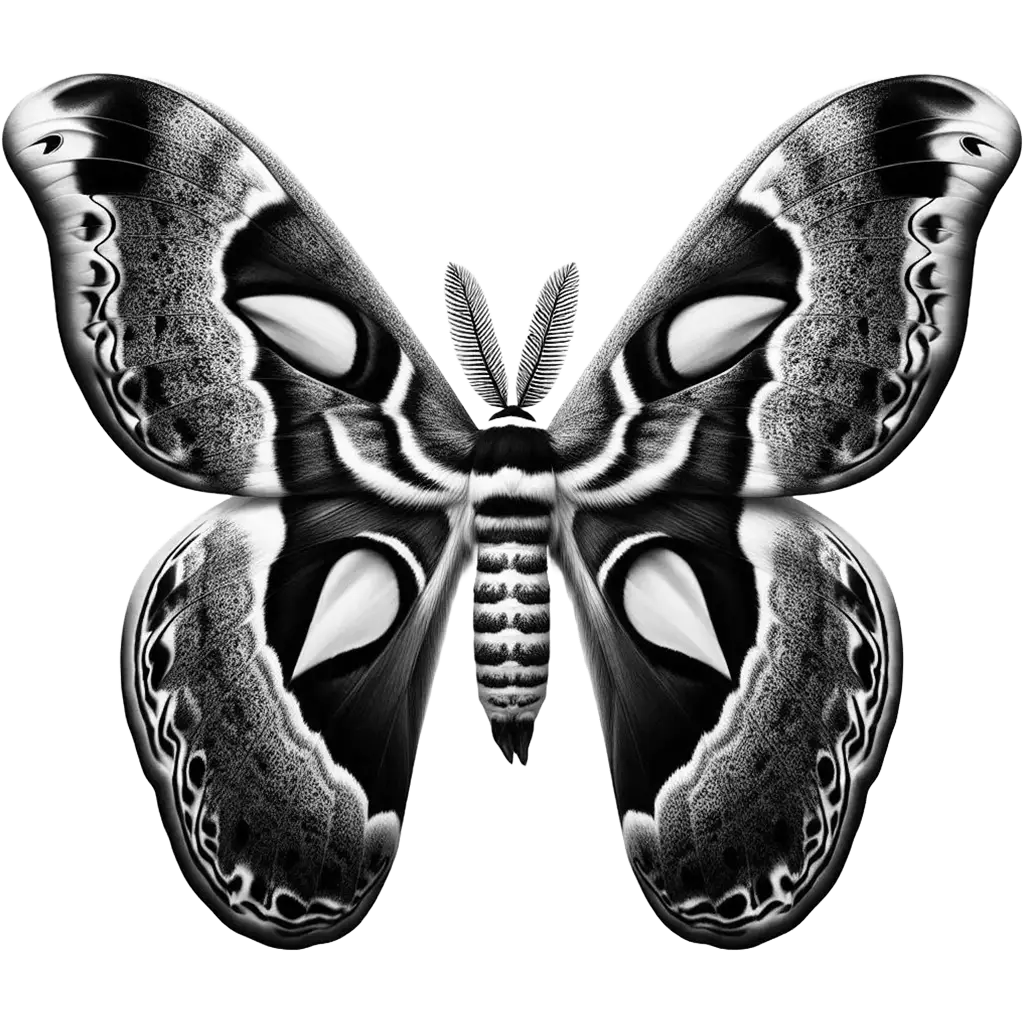
The Giant Peacock Moth, saturnia pyri, is Europe's largest moth, showcasing an impressive wingspan of up to 15 centimeters (6 inches). Its name derives from the eye-catching 'eyes' on its wings, resembling those of a peacock's feathers. These large, circular spots serve as a defense mechanism, deterring predators by mimicking
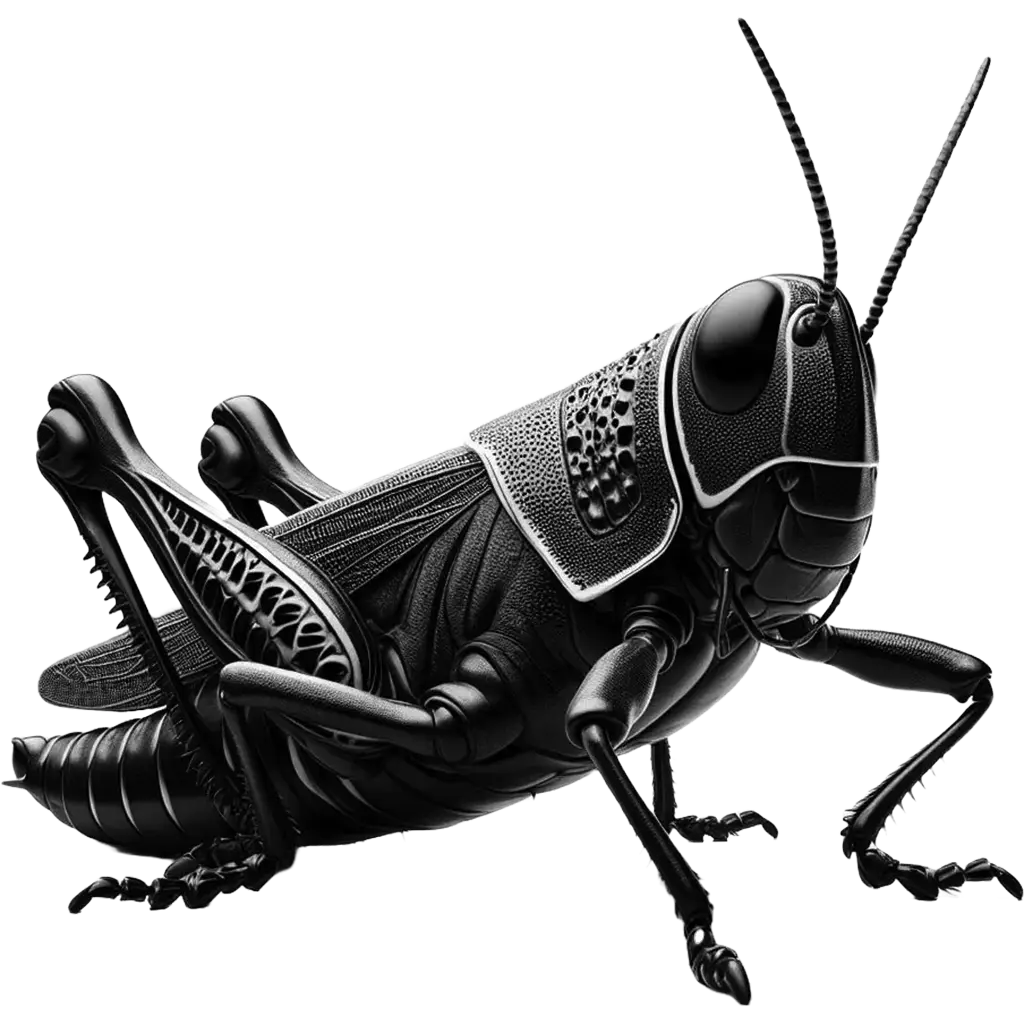

The American Grasshopper, schistocerca americana, is a robust insect known for its sizeable body and striking coloration, which ranges from yellow to olive-green, often with black or brown markings that provide camouflage in their natural grassland habitats. Adults can grow up to 2.5 inches (about 6.35 cm) in length, making
