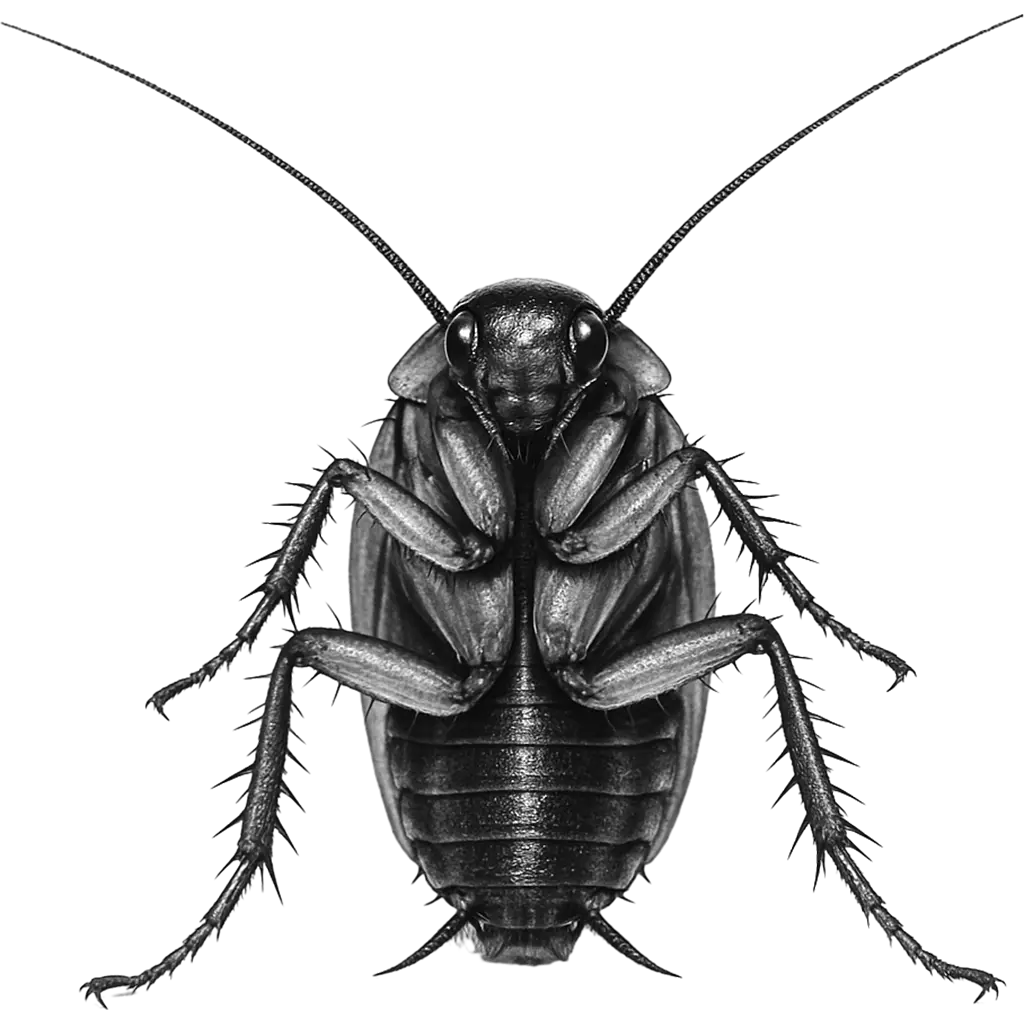

Blattella Germanica
German Cockroach
Human dwellings, kitchens, restaurants, and food processing areas
The German Cockroach displays a compact, oval-shaped body with a light brown to tan coloration that provides effective camouflage in indoor environments. Its exoskeleton is smooth and slightly shiny, complementing a pair of long, delicate antennae that constantly explore the surrounding environment. This small insect measures only a fraction of an inch, yet its agile, swift limbs and flattened profile enable it to slip into even the narrowest of crevices. Overall, its subtle, inconspicuous appearance belies its rapid adaptability.

| Population: | Extremely common in human dwellings globally; thrives in warm, humid urban environments |
| Generation Length: | 2-3 months |
| Average Weight: | 1-2 g |
| Average Length: | 13-16 mm |
| Lifespan: | 1 year in the wild, up to 1.5 years in captivity |
| Diet: | Omnivorous, feeding on diverse organic matter |
| Conservation Status: | Least Concern (LC) |
German cockroaches are nocturnal scavengers that thrive in warm, humid indoor environments, where they exhibit highly active foraging behavior during the night. They are known for their ability to rapidly explore kitchens, bathrooms, and hidden crevices in search of food scraps and moisture. These cockroaches are remarkably resilient and adaptive, frequently forming large congregations in areas where sanitation is poor. Their curious behavior is characterized by continuous exploration and quick, agile movements that allow them to escape potential threats. Although primarily solitary in their movements, they aggregate in favorable conditions, making infestations difficult to control, and their lifestyle is closely linked to human activity.
The German Cockroach subsists on an omnivorous diet, feeding on nearly any organic matter it encounters. This opportunistic insect consumes food scraps, decaying matter, starches, sugars, and proteins from a variety of sources. It forages for crumbs and spills in kitchens, food storage areas, and garbage receptacles, providing a consistent supply of nutrients necessary for its rapid reproduction and energy-demanding lifestyle. In addition, it ingests non-food items such as hair, grease, and glue when available, demonstrating its adaptability in resource-scarce situations. Its efficient digestive system enables it to thrive even in adverse conditions and contributes to unsanitary conditions by spreading bacteria and allergens.
German cockroaches reproduce rapidly through a process of oviposition in which females produce small, protective egg cases called oothecae. Each ootheca contains multiple eggs and is deposited in secure, hidden locations. Mating occurs frequently, with males and females encountering each other in close quarters. This quick reproductive cycle allows infestations to build rapidly and is a key factor in their widespread success.
German cockroaches maintain extraordinarily high population densities in urban areas, particularly in households, restaurants, and food processing facilities. Their numbers can surge rapidly following a single introduction due to their efficient reproductive cycle. Despite extensive control measures, infestations are common and persistent. This remarkable resilience and ability to flourish in diverse microenvironments make them one of the most challenging pests to eliminate.
Classifications
The Key Attributes
Features
- Movement:
Crawling and fast scuttling
- Territorial Behavior:
Not territorial; they aggregate in favorable conditions
- Speed:
Rapid
- Diet:
Omnivorous scavenger
- Physical Features:
- Light brown coloration
- Small, oval body
- Long antennae
- Shield-like pronotum
- Swift, agile legs
- Primary Senses:
- Smell
- Taste
Understanding Habitat and Range
Geography
- Habitat:
Human dwellings, kitchens, restaurants, and food processing areas
- Migration Patterns:
Non-migratory; localized movements
- Geographical Range:
Globally widespread in urban environments
- Climate Preferences:
Warm, humid conditions
Navigating the Wilderness
In the wild
- Predators:
Spiders, ants, and small reptiles
- Prey:
Organic debris and food remnants
- Feeding Behavior:
Forages actively at night in dark, moist areas
- Diet:
Omnivorous, feeding on diverse organic matter
- Defensive Mechanisms:
- Rapid escape
- Nocturnal activity
- Preferred Food Sources:
- Food scraps
- Starchy materials
- Grease
Insights Into Reproduction
Mating
- Mating System:
Promiscuous
- Number of Offspring:
Several dozen eggs per ootheca
- Incubation Period:
45-60 days
- Parental Involvement:
- No parental care; eggs develop within protective oothecae
Youngsters Section
German Cockroach
Fun Fact
German cockroaches are notorious urban pests due to their rapid reproduction and resilience.
These insects have evolved efficient survival strategies, including omnivorous feeding and a prolific breeding cycle, which enable them to thrive even in highly sanitized environments. Their presence often signals underlying sanitation issues.

Download word search puzzles
Word Search Puzzles


Check Out Other Invertebrates

The Cowry Snail, cypraea tigris, often simply referred to as the Tiger Cowry, is a marine gastropod renowned for its highly polished, beautifully patterned shell. This species is widespread across the tropical and subtropical waters of the Indo-Pacific region, from the east coast of Africa, across the Indian Ocean, to
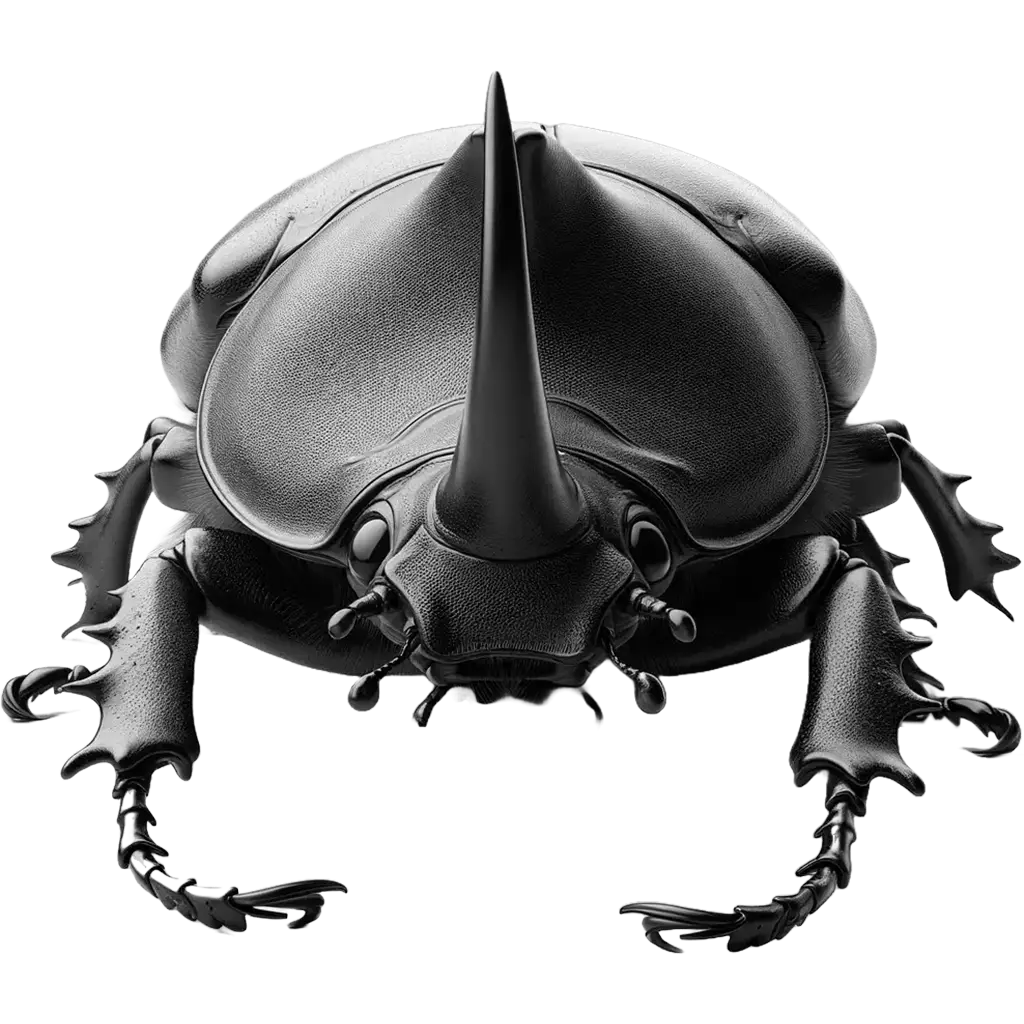

Rhinoceros Beetles, oryctes nasicornis, are among the largest of beetles, with some species reaching up to 15 cm in length, including their distinctive horn-like structures. These beetles are characterized by their impressive size, robust body, and the prominent horns on the males' heads and thoraxes, from which they derive their
Hermit Crabs, coenobita perlatus, are fascinating creatures known for their distinctive habit of living in discarded shells to protect their vulnerable abdomens. Unlike true crabs, Hermit Crabs have soft, asymmetrical abdomens that are not covered by an exoskeleton, making the search for and occupation of empty snail shells critical for
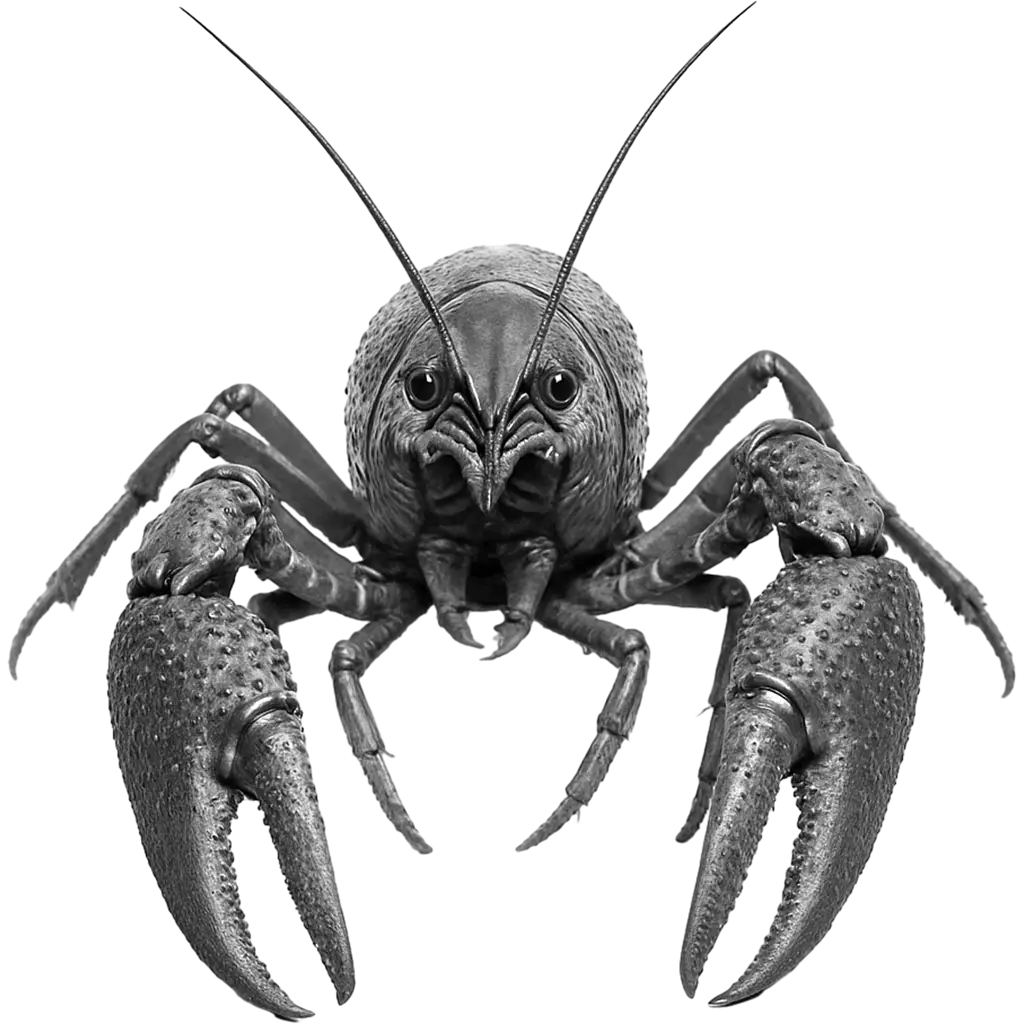

The common yabby is characterized by a robust, segmented body with a sturdy exoskeleton that provides protection. Its limbs are adorned with prominent, clawed pincers and sensitive antennae. The organism features a fan-like tail which aids in swift aquatic movements. Its coloration is usually mottled brown and green, perfectly blending
