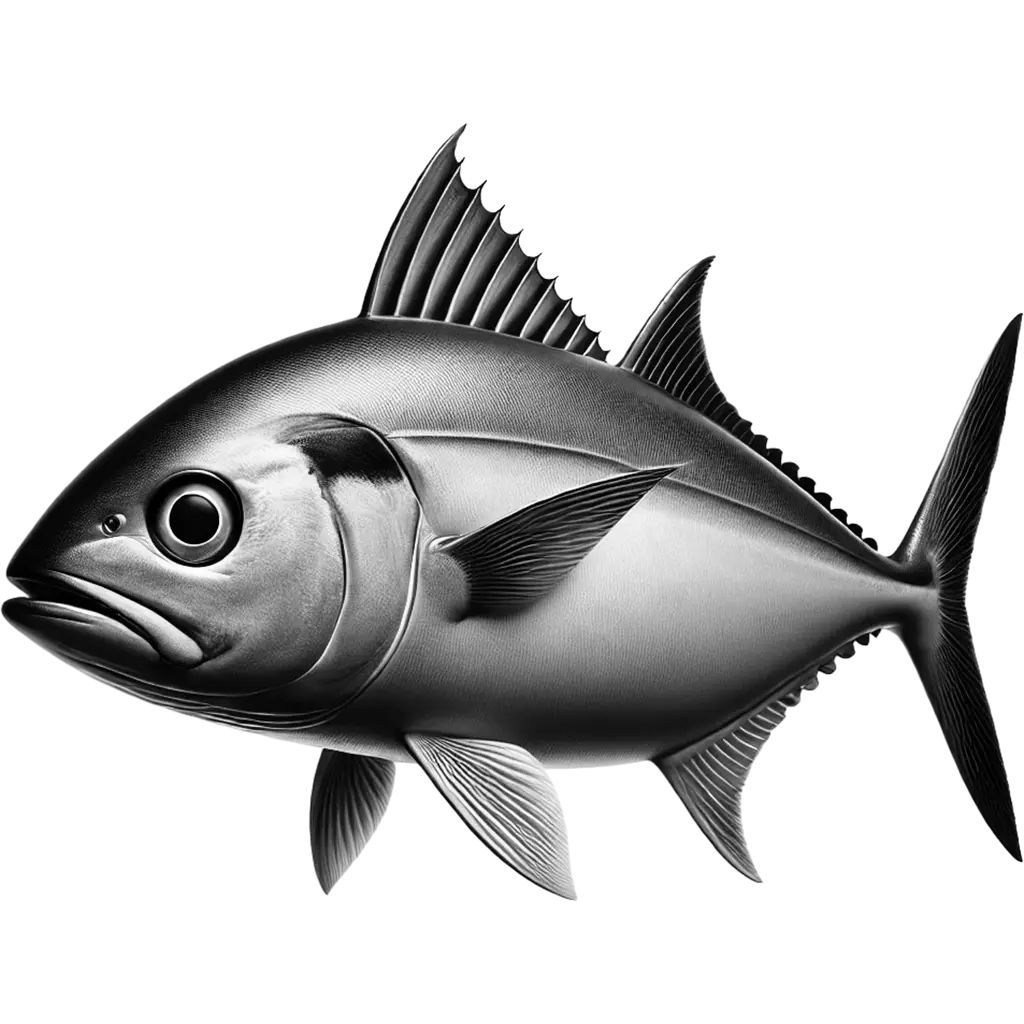

Caranx Rhonchus
False Scad
Continental shelf waters with sandy or muddy substrates; also found in brackish lagoons and estuaries
The False Scad is a moderately large marine fish, reaching up to 60 cm in length and weighing up to 1 kg, though more commonly around 35 cm. It has an elongate, slightly compressed body with a bluish-green to olive green-brown back and a silvery white underside. A narrow yellow stripe often runs from the head to the base of the caudal fin, and distinctive black blotches are present on the operculum and the second dorsal fin lobe. These features, along with its streamlined shape, make it well-adapted to both pelagic and demersal lifestyles.

| Population: | Stable; classified as Least Concern by the IUCN |
| Generation Length: | Approximately 2 years |
| Average Weight: | Up to 1 kg |
| Average Length: | Up to 60 cm; commonly around 35 cm |
| Lifespan: | Up to 5 years |
| Diet: | Carnivorous, with diet shifting from crustaceans to fish as they mature |
| Conservation Status: | Least Concern (LC) |
This schooling species inhabits continental shelf waters with sandy or muddy substrates, typically at depths ranging from 15 to 200 meters. Juveniles are often found in shallower inshore waters, including estuaries, lagoons, beaches, and marshes. The False Scad forms large protective schools, sometimes mingling with other semi-pelagic fishes. Its non-territorial nature and schooling behavior provide safety in numbers, reducing individual predation risk.
As a carnivorous predator, the False Scad's diet includes small fish, crustaceans such as euphausiids, shrimps, and mysids, as well as cephalopods, molluscs, and annelids. Notably, its dietary habits shift with age; younger individuals consume more crustaceans, while adults predominantly feed on small fish. Feeding activity peaks around midday, with minimal nocturnal feeding observed. This diurnal pattern aligns with the availability of prey in its habitat.
Reaching sexual maturity at approximately two years of age, the False Scad spawns in shallow inshore waters. Females, typically measuring between 29 and 35 cm, produce between 480,000 and 990,000 eggs per spawning event. Spawning seasons vary by location but generally occur between April and November. The species is a partial spawner, meaning not all mature eggs are released at once; some are reabsorbed by the female. This reproductive strategy may enhance the chances of successful fertilization and larval survival.
Currently classified as Least Concern by the IUCN, the False Scad maintains a stable population. However, it faces threats from overfishing and habitat degradation. The species holds significant commercial value, especially in regions from Morocco to Senegal, with annual catches ranging from 500 to 19,000 tons. Conservation efforts focus on sustainable fishing practices and habitat preservation to ensure the long-term viability of False Scad populations.
Classifications
The Key Attributes
Features
- Movement:
Pelagic and demersal; forms schools
- Territorial Behavior:
Non-territorial; schooling species
- Speed:
Not specified
- Diet:
Carnivore
- Physical Features:
- Elongate, slightly compressed body
- Bluish-green to olive green-brown back
- Silvery white underside
- Narrow yellow stripe from head to caudal fin base
- Black blotch on operculum
- Black blotch with narrow pale margin on second dorsal fin lobe
- Primary Senses:
- Sight
Understanding Habitat and Range
Geography
- Habitat:
Continental shelf waters with sandy or muddy substrates; also found in brackish lagoons and estuaries
- Migration Patterns:
Non-migratory
- Geographical Range:
Eastern Atlantic Ocean from Namibia to Spain; throughout the Mediterranean Sea
- Climate Preferences:
Tropical and temperate
Navigating the Wilderness
In the wild
- Predators:
Larger predatory fish
- Prey:
Small fish, crustaceans (euphausiids, shrimps, mysids), cephalopods, molluscs, annelids
- Feeding Behavior:
Diurnal feeder; peak activity around midday
- Diet:
Carnivorous, with diet shifting from crustaceans to fish as they mature
- Defensive Mechanisms:
- Schooling behavior for protection
- Preferred Food Sources:
- Small fish
- Crustaceans
- Cephalopods
Insights Into Reproduction
Mating
- Mating System:
Not specified
- Number of Offspring:
Females produce between 480,000 and 990,000 eggs per spawning event
- Incubation Period:
Not specified
- Parental Involvement:
- Not specified
Youngsters Section
False Scad
Fun Fact
Despite its name, the False Scad is a true member of the jack family, Carangidae.
The name 'False Scad' arises from its resemblance to species in the scad genera Decapterus and Trachurus, but detailed anatomical analysis places it firmly within the Caranx genus.

Download word search puzzles
Word Search Puzzles


Check Out Other Fish
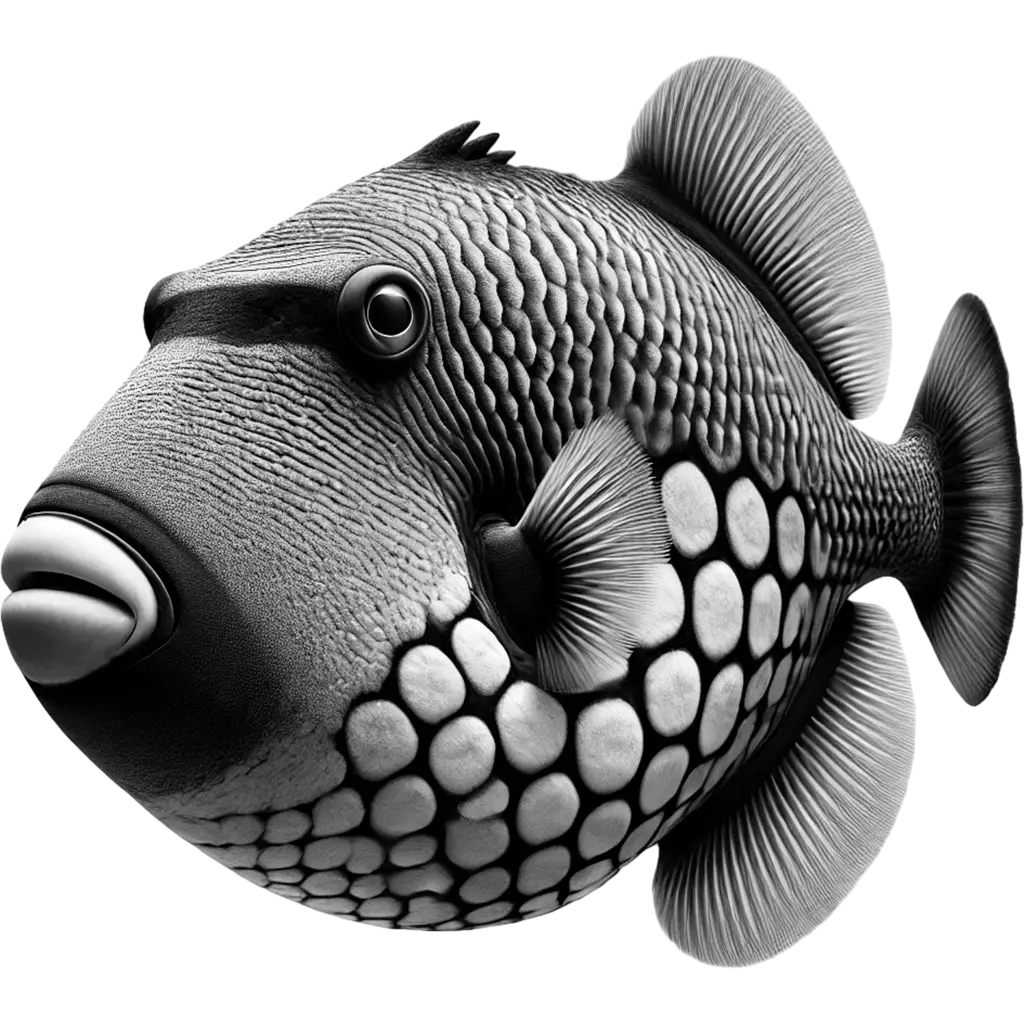

The Blackbelly Triggerfish exhibits a robust, laterally compressed body adorned with striking patterns and a distinctive black belly contrasting with vibrant hues on its fins and upper body. Its rough, textured skin and prominent dorsal 'trigger' spines not only define its appearance but also serve as a defense mechanism. With
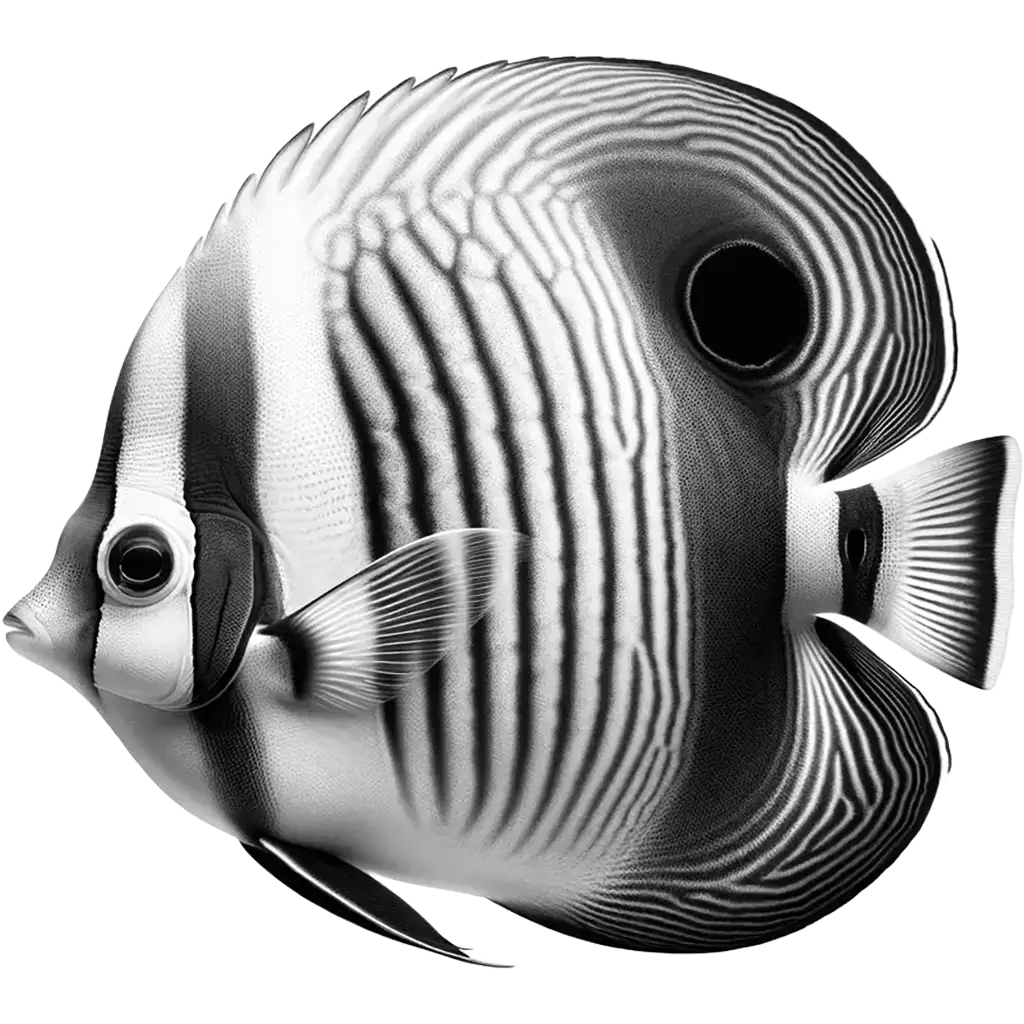

The Oval Butterflyfish, chaetodon lunulatus, is a vibrant and colorful marine species renowned for its striking appearance and widespread distribution across the Indo-Pacific region. This species exhibits a deep, flattened body typical of butterflyfish, reaching up to 20 cm (about 8 inches) in length. The body coloration is predominantly yellow
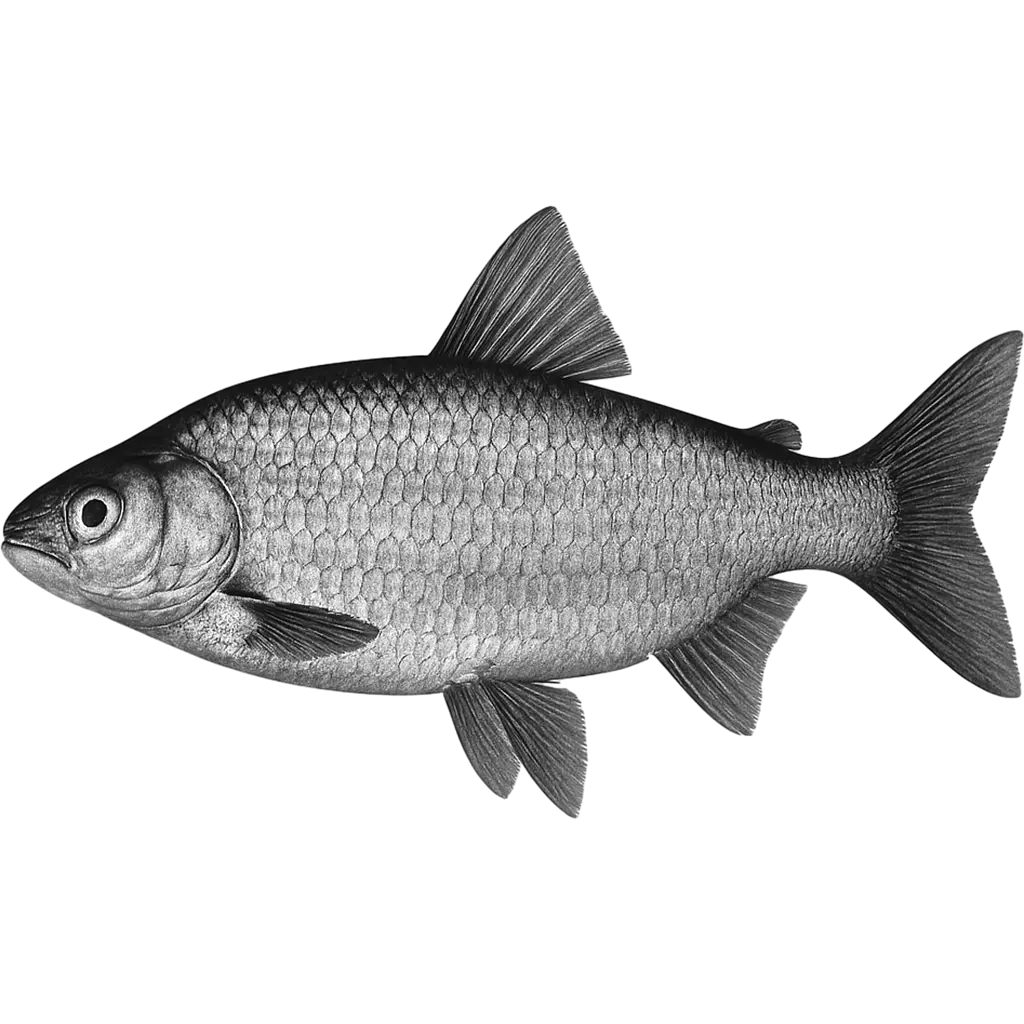

The Gwyniad displays an elegant and streamlined body, characterized by a slender, laterally compressed shape that enhances its buoyancy in clear, deep waters. Its skin glistens with a silvery sheen that reflects subtle hints of pale blue, while delicate, reflective scales form a smooth, almost ethereal surface. A gently rounded
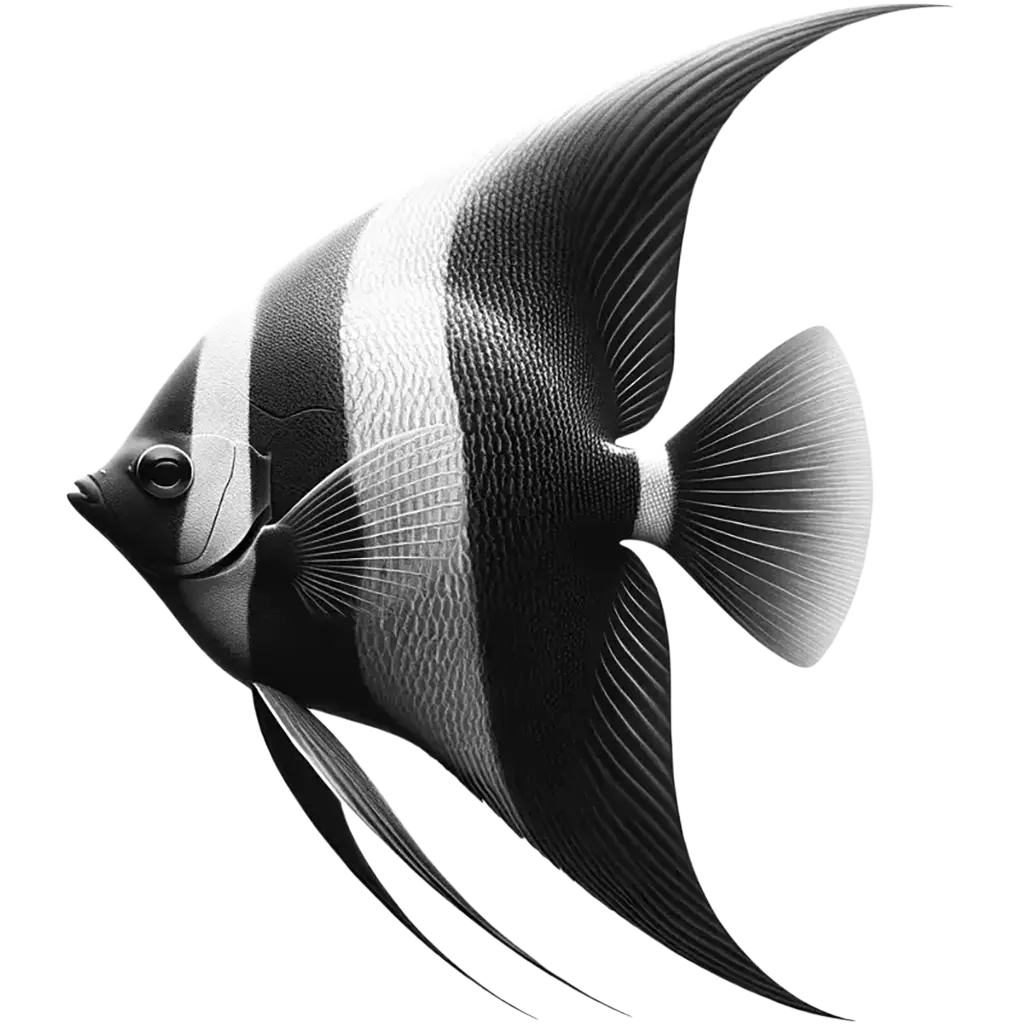
The Deep Angelfish, pterophyllum altum, also known as the Altum Angelfish, is a striking freshwater fish native to the Orinoco and Amazon basins of South America. It is the largest species within the Pterophyllum genus, with adults capable of reaching up to 18 cm in height and 15 cm in
