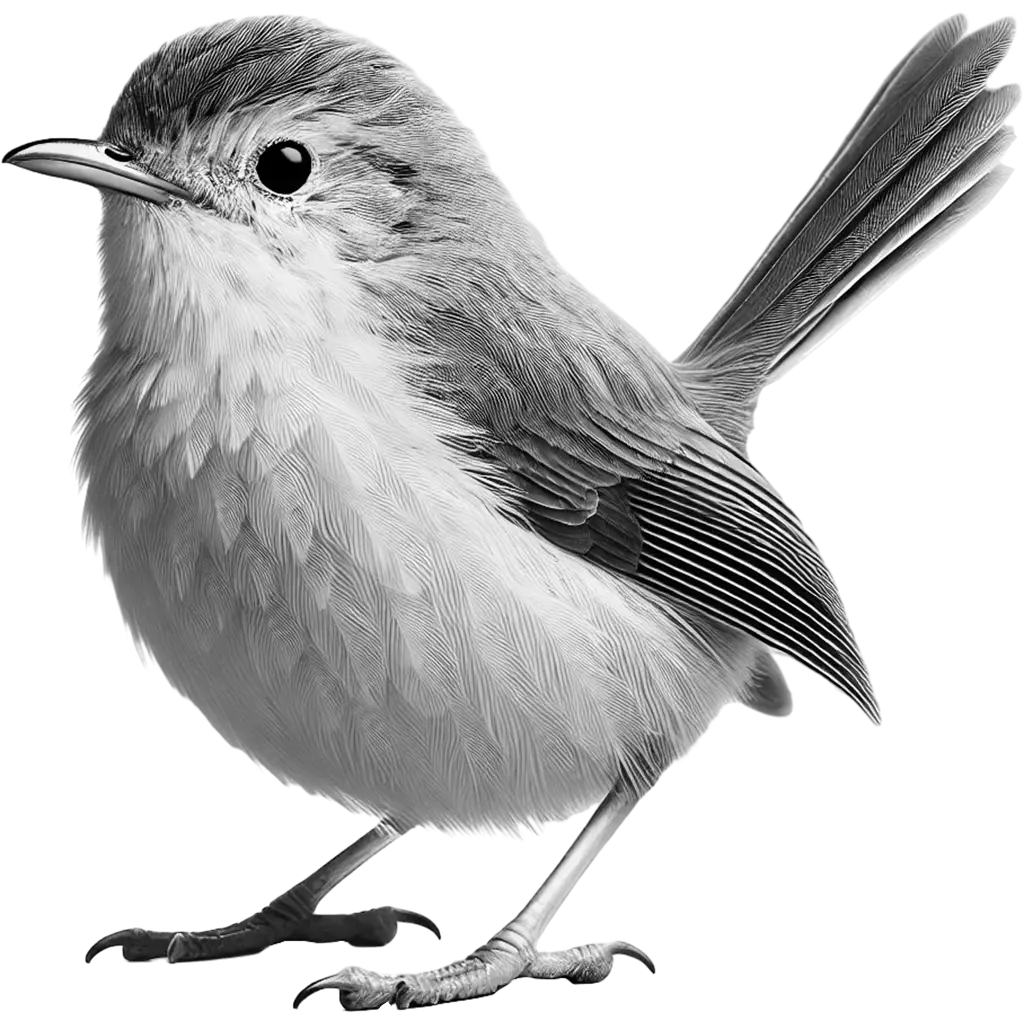

Prinia Somalica
Pale Prinia
Arid scrublands, open grasslands, and dry savannas across parts of East Africa
The Pale Prinia is a diminutive bird characterized by its soft, pale plumage that ranges from light gray to off-white. Its slender body is accentuated by subtle streaks along its wings and back, while a delicate, pointed bill and long, tapering tail contribute to its refined, graceful appearance. The bird's gentle facial features and expressive eyes add to its understated charm, allowing it to blend seamlessly into its arid scrubland habitat.

| Population: | Common in East Africa's scrub and grasslands but faces population declines from habitat loss and overgrazing |
| Generation Length: | Approximately 2.5 years |
| Average Weight: | Approximately 8-10 grams |
| Average Length: | Approximately 10-12 cm |
| Lifespan: | Approximately 2-3 years in the wild; up to 4 years in captivity |
| Diet: | Omnivorous, mainly insectivorous, supporting a high-energy lifestyle and aiding pest control |
| Conservation Status: | Least Concern (LC) |
In its native arid and semi-arid environments, the Pale Prinia is an active and agile forager. It is often observed flitting between low shrubs and grasses, where its quick, darting movements help it navigate the sparse vegetation. The bird's behavior is marked by a constant search for food, punctuated by brief pauses to listen and scan its surroundings, a vital strategy for avoiding predators in open landscapes.
The diet of the Pale Prinia is primarily insectivorous, with a strong reliance on small insects and arthropods that it expertly captures among the undergrowth. Occasionally, it supplements its diet with seeds and berries, particularly during periods when insects are scarce. This varied foraging strategy not only sustains its energetic lifestyle but also plays an important role in natural pest control and seed dispersal within its ecosystem.
During the breeding season, the Pale Prinia becomes more vocal and territorial. Males defend small territories with soft, melodious calls and engage in brief, intricate courtship displays to attract females. Once paired, the duo cooperates in building a modest nest and incubating a clutch of 3-5 eggs. This intimate period of reproduction ensures the successful nurturing and development of the chicks in a challenging, arid environment.
Although generally common within its restricted range, the Pale Prinia faces ongoing threats from habitat degradation and overgrazing. Localized declines highlight the need for habitat conservation and sustainable land management practices to maintain stable populations of this subtle yet ecologically important bird.
Classifications
The Key Attributes
Features
- Movement:
The Pale Prinia is an active and agile flier, frequently darting through low scrub and grass. It moves with quick, erratic bursts that allow it to evade predators and navigate its open, arid habitat.
- Territorial Behavior:
Males are notably territorial during the breeding season, defending small areas with soft calls and subtle displays.
- Speed:
Capable of rapid, agile maneuvers when foraging or escaping threats.
- Diet:
Primarily insectivorous, feeding on small insects, spiders, and other arthropods gleaned from the ground and low vegetation. They may also consume seeds and berries when insects are less abundant.
- Physical Features:
- Small, slender body with soft, pale plumage ranging from light gray to off-white
- Subtle streaks along the wings and back
- Delicate, pointed bill and a long, tapering tail
- Expressive, small eyes that lend a gentle appearance
- Primary Senses:
- Sight
- Hearing
Understanding Habitat and Range
Geography
- Habitat:
Arid scrublands, open grasslands, and dry savannas across parts of East Africa
- Migration Patterns:
Non-migratory; individuals make only short local movements in response to seasonal food availability.
- Geographical Range:
Restricted to select regions in East Africa, including parts of Somalia, Ethiopia, and Kenya.
- Climate Preferences:
Prefers arid to semi-arid climates with hot, dry conditions punctuated by brief rainy seasons.
Navigating the Wilderness
In the wild
- Predators:
Small raptors, snakes, and other small carnivorous birds may prey on juveniles and eggs.
- Prey:
Feeds primarily on insects and small arthropods, with occasional consumption of seeds and berries.
- Feeding Behavior:
Forages by hopping between low vegetation and gleaning insects from leaves and ground litter. Its quick, darting movements are key to capturing fast-moving prey.
- Diet:
Omnivorous, mainly insectivorous, supporting a high-energy lifestyle and aiding pest control
- Defensive Mechanisms:
- Utilizes rapid, erratic flight and excellent camouflage to evade predators
- Preferred Food Sources:
- Small insects, spiders, and other arthropods found among low scrub
Insights Into Reproduction
Mating
- Mating System:
Generally monogamous during the breeding season, with males displaying territorial behaviors to attract females.
- Number of Offspring:
Typically 3-5 eggs are laid per clutch.
- Incubation Period:
Eggs hatch after approximately 12-14 days of incubation.
- Parental Involvement:
- Both parents contribute to nest building and feeding the chicks until they fledge.
Youngsters Section
Pale Prinia
Fun Fact
The Pale Prinia's soft, melodious calls are a familiar sound in East African scrublands, adding a gentle soundtrack to the arid landscape.
Despite its delicate appearance, this tiny bird plays a key role in controlling insect populations and dispersing seeds, contributing to the health and diversity of its ecosystem.

Download word search puzzles
Word Search Puzzles


Check Out Other Birds
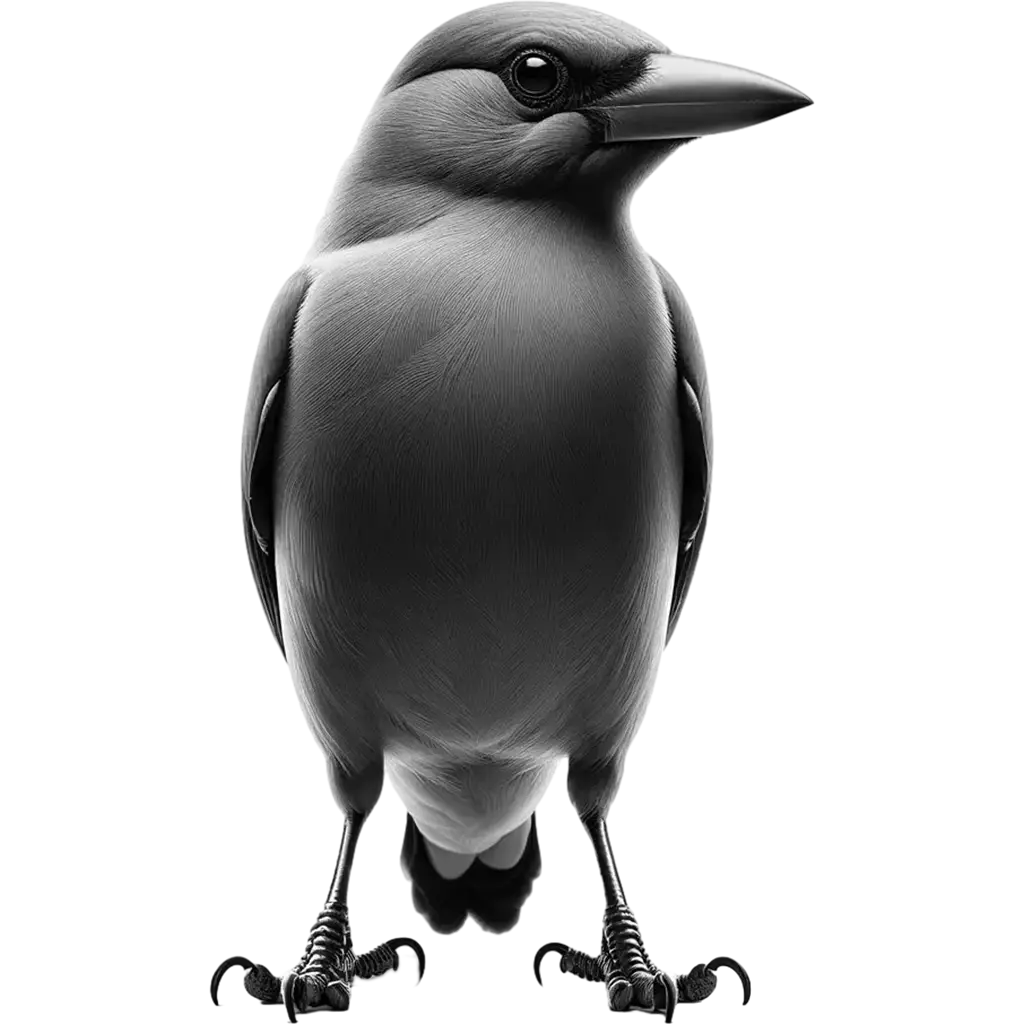

The Red-Billed Oxpecker, buphagus erythrorynchus, is a small bird native to sub-Saharan Africa, easily recognized by its distinctive red bill and yellow ring around the eyes. This species exhibits a predominantly brown plumage with lighter underparts, allowing it to blend into the savannah and woodland habitats it frequents. Adults can
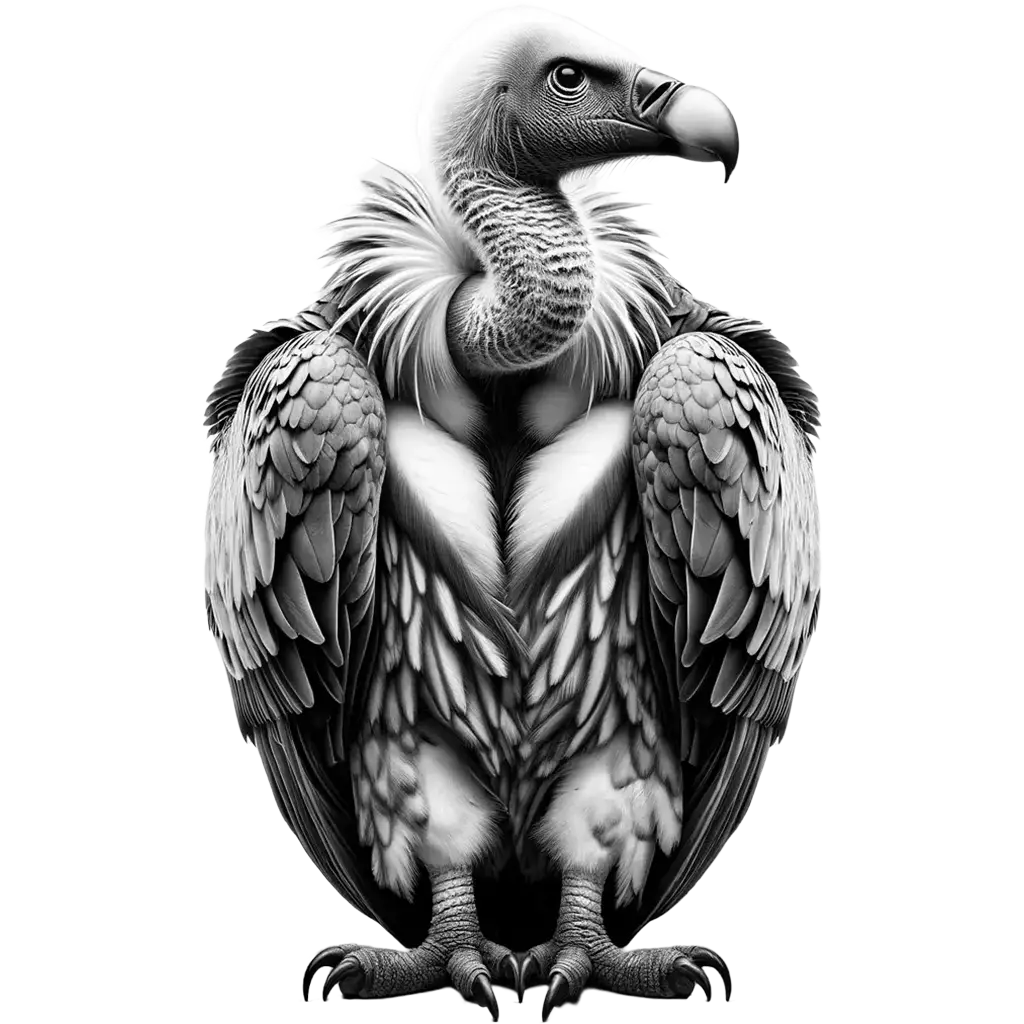
Rüppell's vulture, gyps rueppelli, named after the German naturalist Eduard Rüppell, is a large and critically endangered bird of prey residing predominantly in the Sahel region of Africa. This species stands out due to its impressive size, with a length of up to 1 meter and a wingspan reaching nearly

The Black Swan, cygnus atratus, is a large waterbird native to Australia, easily distinguished by its mostly black plumage and striking red bill with a white band. It measures between 110 to 142 centimeters in length and has a wingspan of up to 2 meters, making it one of the
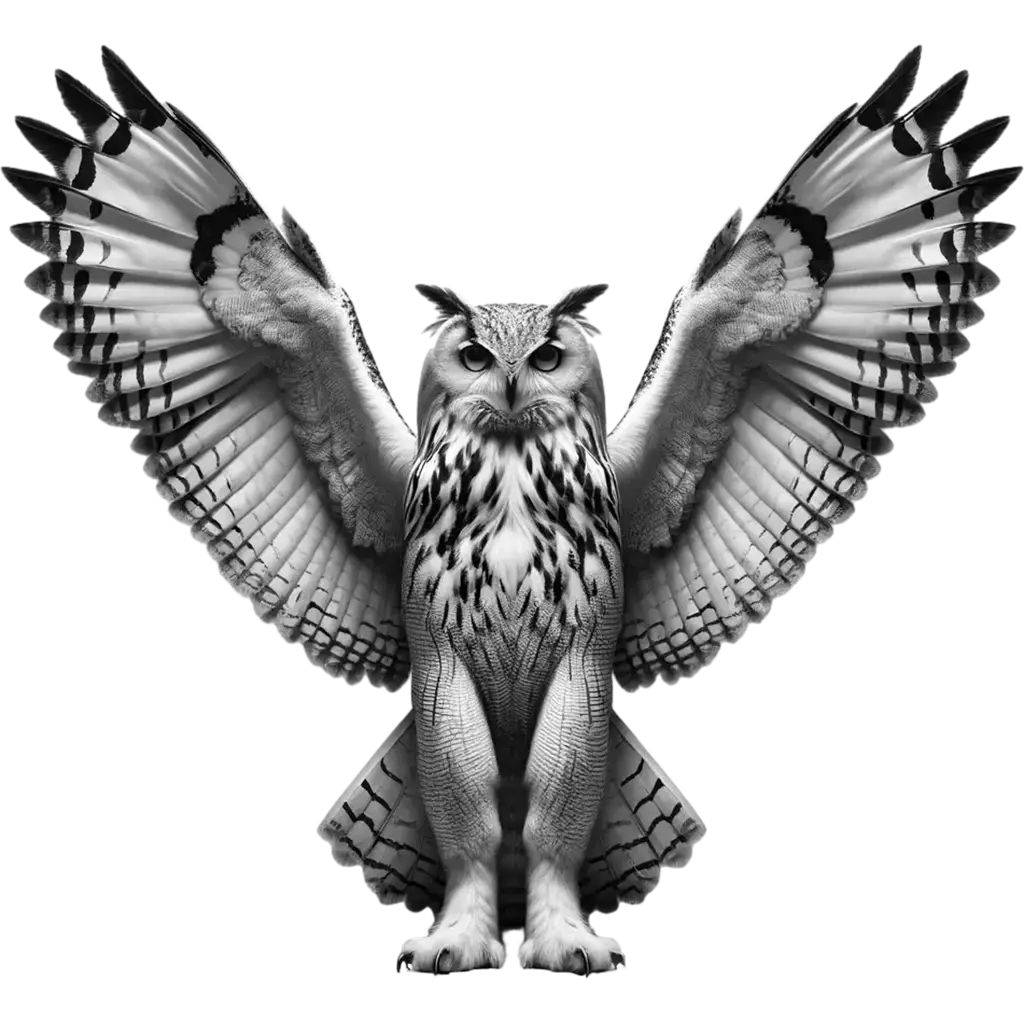

The Eurasian Eagle-Owl, bubo bubo, is one of the largest and most powerful owl species, with a widespread distribution across Europe, Asia, and parts of North Africa. This majestic bird is notable for its large size, with a wingspan that can reach up to 2 meters (6.6 feet), and a
